In 2025, choosing between eCommerce platforms fees like navigating a crowded marketplace. Every option claims to be powerful, flexible, and built for growth; Miva Merchant vs Shopify are no exception!
One is recognized for its technical freedom and enterprise-level control; the other has become the go-to choice for merchants who want a fast, scalable setup. To help you understand which one truly fits your business between these two, we break down Miva vs Shopify across:
- eCommerce features
- Ease of use
- Customization
- Scalability
- SEO & marketing
- Apps and integrations
- Customer support
- Security
- Pricing
Let's get started!
Miva Merchant vs Shopify: A Quick Overview
Understanding Miva Merchant
Miva Merchant is an enterprise-focused eCommerce platform that allows merchants to tailor both the front-end and backend in highly specialized ways.
Because of its technical nature, Miva does not attract the same volume of mainstream adoption as Shopify. The platform reportedly serves 5,400+ active merchants (according to BuiltWith), with most of them being mid-sized to large enterprises that rely heavily on advanced customization and structured development workflows.
Miva Merchant Pros | Miva Merchant Cons |
Exceptionally flexible customization, including backend logic and server-level control | Requires technical setup; no instant onboarding |
Industry-leading inventory rules, quantity limits, and catalog structure | Limited payment gateway options out of the box |
Advanced SEO capabilities with open templating and URL control | Much smaller app ecosystem with fewer ready-made tools |
Direct human customer support and strong documentation | Pricing is opaque and generally higher than Shopify |
High backend freedom via MivaScript, JSON API, and SFTP access | Better suited for enterprise teams, not general merchants |
Understanding Shopify
Shopify, on the other hand, is one of the world’s most widely used ecommerce platforms, powering more than 7 million active stores globally (according to BuiltWith).
Its appeal stems from its ease of use, fully managed infrastructure, large app ecosystem, and simple pricing model. Businesses of every size, from new entrepreneurs to household-name enterprises, choose Shopify because it provides a clean, intuitive experience and requires no technical expertise to launch or scale an online store.
Shopify Pros | Shopify Cons |
Extremely easy onboarding; no technical setup required | Limited backend control compared to Miva |
Broadest payment gateway support, including Shopify Payments | Checkout customization restricted unless on Shopify Plus |
Fully hosted, automatically scalable, and highly stable | App ecosystem introduces third-party dependency risks |
More than 13,000 apps for extending functionality instantly | SEO control is strong but less open-ended than Miva |
Transparent pricing with predictable monthly costs | Support is increasingly self-service–oriented |
Miva Merchant vs Shopify: Which Is Better?
Based on our findings, Shopify ultimately emerges as the stronger choice for the majority of businesses. Its ease of use, extensive payment options, unmatched app ecosystem, automatic scalability, predictable pricing, and stable managed infrastructure make it far more accessible and practical for general merchants.
Nevertheless, Miva Merchant undeniably outperforms Shopify in areas such as deep customization, advanced SEO, catalog complexity, and direct human support. Below is a summarized comparison table reflecting the core criteria examined in our article:
Criterion | Miva Merchant | Shopify | Winner |
Inventory Management | Exceptionally advanced rules, limits, and catalog structure | Robust but less flexible; variant limit and fewer native rules | Miva Merchant |
Payment Gateways | Limited built-in options; relies on custom modules | 100+ gateways plus Shopify Payments | Shopify |
Shipping | Highly configurable rules and conditions | Equally strong with flexible zones and carrier rates | Tie |
Ease of Use | Technical, manual setup; requires expertise | Instant onboarding; intuitive dashboard | Shopify |
Customization | Back-end and front-end fully open | Strong but more controlled; limits on back-end logic | Miva Merchant |
Scalability | Best for enterprise teams with developers | Automatic cloud scalability for all merchants | Shopify |
SEO & Marketing | More advanced SEO control | Strong marketing + standard SEO features | Miva Merchant |
Apps & Integrations | Fewer than 20 modules | 13,000+ apps; broad ecosystem | Shopify |
Customer Support | Direct human support; highly responsive | Increasingly self-service | Miva Merchant |
Security | Secure but depends on hosting quality | Fully managed, enterprise-grade security | Shopify |
Pricing | No clear tiers; estimated from $100 to $600/month | Clear tiers from $39/month to $2,300+ | Shopify |
Keep reading to see how each criterion plays out side-by-side!
Miva Merchant vs Shopify eCommerce Features (A tie)
The Verdict: The comparison ultimately balances out. Miva brings exceptional depth in catalog structure, custom rules, and inventory sophistication. Shopify, on the other hand, excels with broader payment gateway availability and a more streamlined operational ecosystem that appeals to a wide audience.
Even so, this tie between Miva Merchant vs Shopify reflects two very different strengths rather than similarity. Below is a closer, more detailed breakdown of where each one stands out:
Inventory management (Miva Merchant wins)
From our observation, Shopify offers a mature, highly serviceable inventory management system that can support merchants throughout their growth.
Specifically, you can create unlimited products and assign multiple variants for attributes like size or color (though Shopify does impose a 100-variant limit per product).
Inventory is tracked at the variant level and automatically updated when orders are placed, ensuring accurate stock representation as the store operates. Better yet, organizing large catalogs is relatively easy thanks to Shopify’s use of collections, tags, and additional metadata, which help maintain clarity even in stores with thousands of SKUs.
On the other hand, one area where Shopify shows its boundaries is purchase-limit control. Since Shopify does not provide built-in minimum or maximum quantity rules per customer, you'll likely need to turn to third-party apps or custom development to enforce these restrictions.
How about Miva Merchant? Miva not only matches Shopify's core capabilities but also significantly expands upon them.
Like Shopify, Miva also supports an unlimited number of products. Yet, it goes even further than that by allowing unlimited categories and multi-level sub-categories. Product data can be enriched through custom fields such as SKU, UPC, ISBN, or manufacturer details, and merchants can use either text or HTML for detailed descriptions.
And that's not all; the platform enhances merchandising capabilities with related products, dynamic product relationships, and support for bundles or kits. It also incorporates native order-level purchase controls, allowing merchants to enforce minimum order quantities or values directly within checkout.
Most importantly, what truly distinguishes Miva is its built-in control over quantity limits. With the official “Quantity Limits” module, merchants can define minimum and maximum purchase quantities globally, by category, per product, or even per variant (if conflicting rules appear, Miva automatically applies the strictest one).
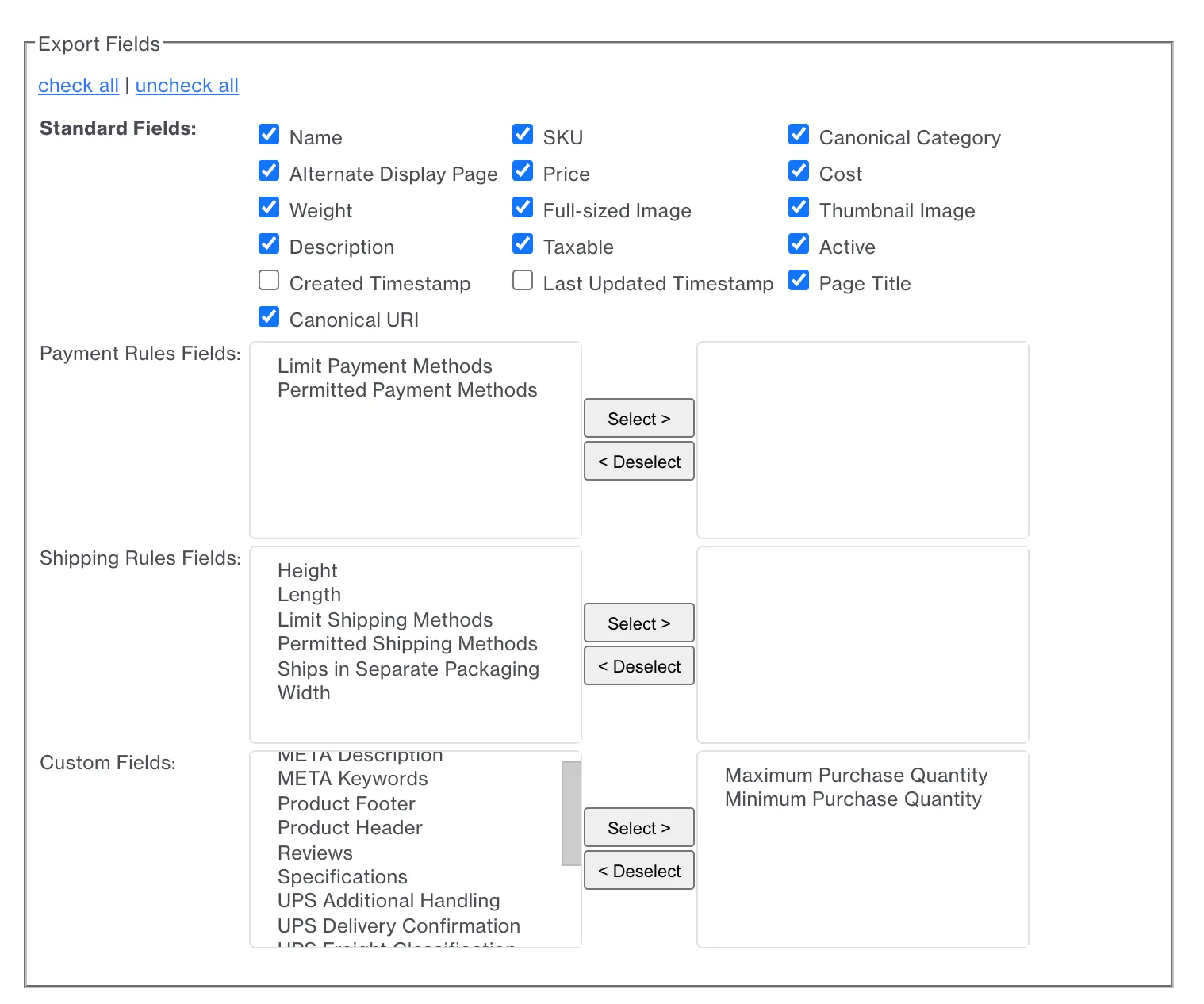
Plus, for large-scale or integrated operations, Miva’s JSON-based product-management API supports batch operations, complex variant management, and real-time syncing with warehouse solutions such as SkuVault Core. Taken together, such control and flexibility make Miva the stronger choice for intensive inventory and catalog management, especially where custom rules or complex structures are required.
Payment gateways (Shopify wins)
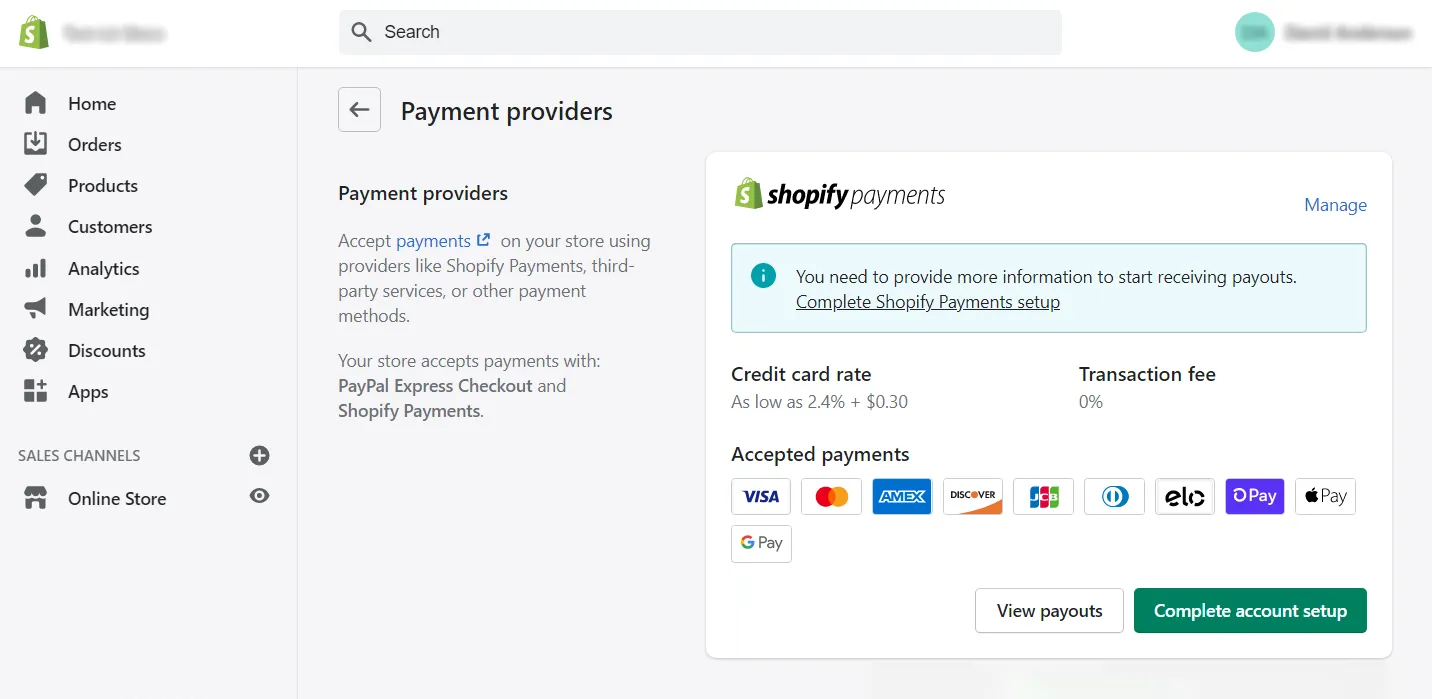
When it comes to payments, Shopify takes the lead with a noticeably broader offering.
Shopify Payments, its native gateway, allows merchants to accept major card payments directly within the platform and removes the need for external configuration entirely. This payment option alone reduces friction for many stores, especially those operating in regions where Shopify Payments is available.
In addition, beyond its native solution, Shopify supports more than 100 third-party payment providers around the world. Its integrations cover both direct providers, where checkout remains on the storefront, and external providers that redirect customers to a hosted payment page.
On the other hand, Miva Merchant's official list of supported payment gateways only has roughly nine options, including:
- MivaPay (powered by PayPal)
- Square
- PayPal Complete Payments
- CyberSource
- Chase Paymentech
- Braintree
- Authorize.Net
- Apple Pay
- Amazon Pay v2
- Affirm
Since Miva does allow custom modules, the total number of gateways in reality is actually larger than this “official” list, depending on custom work. Nevertheless, merchants expecting plug-and-play payments will likely find Shopify to hold a clearer advantage in this category.
Shipping (A tie)
Shipping is an area where both Miva Merchant vs Shopify perform at a similarly high level.
Specifically, Miva Merchant provides a deeply configurable shipping system suitable for businesses with complex logistics requirements. Merchants can:
- Create static shipping methods such as flat-rate, fixed-rate, or free shipping, or connect real-time carrier modules to fetch dynamic quotes from UPS, USPS, FedEx, and others.
- Use a rich set of conditional rules that determine when shipping methods appear. These rules can factor in order subtotal, total weight, number of items, postal codes, or geographic boundaries.
- Exclude specific methods under certain conditions (for example, blocking a carrier for P.O. Box addresses) or define dependencies that prevent certain options from appearing together.
- Customize display, e.g., renaming methods, adjusting their order in the checkout flow, or modifying carrier rates with percentage or fixed adjustments.
Not to mention, integrations like ShipStation and ShipWorks, Miva stores can create batch labels, support multiple carriers, and synchronize tracking data back into the system.
Similarly, Shopify also matches Miva's capabilities when it comes to shipping power. Merchants can:
- Configure flat-rate, free-shipping, price-based, and weight-based rules, as well as offer local delivery or local pickup for customers nearby.
- Use carrier-calculated shipping rates when connected to compatible providers or when using third-party shipping applications.
- Define shipping zones with meticulous granularity, including region-specific or postal-code-specific pricing tiers.
Shopify’s built-in fulfillment tools simplify day-to-day operations through label printing, package dimensions, and consolidated order management. We also find international shipping to be quite well supported, with an extensive ecosystem of apps and carriers capable of handling customs and global rate calculations.
Ease of Use (Shopify wins)
The Verdict: Shopify allows anyone to create an account within seconds, jump straight into a clean dashboard, and begin building a store right away. Miva, by comparison, involves a more technical setup process that feels significantly less accessible to beginners.
This difference between Miva Merchant vs Shopify becomes even more apparent once you examine how each platform handles onboarding and day-to-day store management. Let's break down what the experience looks like for new users on both systems:
Shopify's ease of use
All in all, getting started is incredibly simple on Shopify.
From the beginning, you can easily and instantly create an account using your Gmail, Apple, or Facebook login, which automatically unlocks a three-day free trial. Shopify also asks for optional information during onboarding (such as your business type or preferred payment setup), but you can skip all of these steps and access your dashboard immediately.
Once inside, you will finđ the interface clean, modern, and highly intuitive. Navigation is anchored by a left-hand sidebar that organizes all major sections of your store: Products, Orders, Customers, Analytics, Online Store, and more. This layout ensures that users always know where to go, be it adding new inventory, adjusting pricing, or reviewing store performance!
Miva Merchant's ease of use
Miva Merchant, by contrast, does not offer an instant setup path.
Specifically, unlike with Shopify, you cannot simply click a button to create an account or start a trial. Instead, both demo access and account creation require you to contact the Miva team directly, which introduces more steps before you can even begin.
Setting up a Miva store also feels more technical and less streamlined than Shopify. To get started, you first obtain a developer account, install the Miva software on your server, and then use the admin panel to enable eCommerce functionality for your domain.
From there, you must configure essential components such as products, payments, and shipping, often by installing and activating additional modules. And that's not all; to add another store to an existing setup, you must acquire the Additional Storefront License, which lets you spin up multiple stores from the same admin environment.
As mentioned earlier, the Miva team does guide users throughout onboarding, which helps smooth out the rough edges. Nevertheless, at the end of the day, the platform is still far from “easy” in the way Shopify is.
Customization (Miva Merchant wins)
The Verdict: Miva Merchant ultimately takes the win as it gives developers far more freedom across both the front-end and backend levels. That said, Shopify (especially Shopify Plus) is already an outstandingly customizable platform for most businesses.
In practice, many merchants may not even need the extra layers of flexibility Miva provides unless their workflows, integrations, or storefront behaviors require deep technical tailoring. To see how Miva Merchant vs Shopify differ, let's break down what customization actually looks like on each:
Shopify’s customization
Shopify approaches customization through a multi-layer system:
- A templating language (Liquid)
- Fully open front-end code
- Modular theme architecture
- APIs for back-office logic
- Shopify Functions for custom commerce rules
- Apps for extended behavior
- Headless development options for complete storefront control.
As you can see, the foundation is Liquid, Shopify’s proprietary templating language. Liquid controls how content is displayed on storefront pages, allowing developers to loop through products or collections, conditionally render dynamic content, work with metafields, and build reusable sections and blocks.
However, while Liquid is powerful at the presentation layer, it intentionally cannot execute backend logic, write to the database, make direct API calls, or run asynchronously. Such limitations help maintain platform stability but also mean that Liquid is more restrictive compared to Miva’s templating system.
Beyond Liquid, developers have full freedom with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Shopify does not restrict which front-end technologies you use, so you can incorporate vanilla JS, modern frameworks like Alpine.js, Vue, or React (with hydration), and build interactive UI elements ranging from AJAX carts to dynamic filtering or modal experiences. The only area with a hard boundary is the checkout: JavaScript cannot modify checkout pages unless you are on Shopify Plus, where checkout.liquid or Checkout Extensibility becomes available.
Similarly, modern Shopify themes are built using JSON templates, Liquid sections, and dynamic blocks. The Admin API (REST or GraphQL) supports back-office operations like product management, order handling, fulfillment workflows, customer data updates, and metafields. At the same time, the Storefront API powers custom storefronts, headless architectures, and mobile apps, while webhooks let developers automate workflows triggered by events such as new orders or product updates.
For full control of the storefront, Shopify offers Hydrogen and Oxygen, its React-based headless framework and hosting platform. These tools let developers build entirely custom UX while still connecting to Shopify’s backend for product and checkout functionality. Still, keep in mind that despite all these advantages, headless architecture replaces only the front-end, not Shopify’s underlying commerce engine.
Miva Merchant’s customization
Miva Merchant does offer the standard theme tools that let users change colors, fonts, headers, and other basic visual elements.
However, its true strength lies in its extensive technical customization capabilities. Unlike Shopify, which reserves deeper backend control for limited contexts, Miva opens nearly every part of the platform to developers!
At the core is MVT, Miva’s templating language. Similar in concept to Liquid or Twig but significantly more capable, MVT can interact deeply with store data, variables, customer information, category structures, pricing rules, and more. Developers can rewrite almost any storefront behavior by modifying templates for product pages, categories, checkout, baskets, or account areas. Complex conditional logic, custom layouts, and dynamic content can all be built directly within templates without touching backend code.
On the front-end, Miva also imposes no restrictions. Developers can add custom CSS and JavaScript, embed modern frameworks like React, Vue, or Svelte, and build SPA-like components, AJAX-driven interactions, or completely custom UI systems. Unlike Shopify, where Liquid limits what JavaScript is allowed to access, Miva’s front-end environment gives developers full control.
Better yet, beyond templating, Miva offers MMUI and ReadyTheme customization that enable deep modification of layout components, snippets, includes, and template-level frameworks. Not to mention, MivaScript, the platform’s server-side language, allows developers to create custom logic, build new API endpoints, manipulate store data, and develop specialized admin tools.
We are also impressed that Miva provides a robust JSON API for external integrations. It enables reading and writing product, order, customer, pricing, attributes, and fulfillment data; automating catalog imports; synchronizing with enterprise systems; and triggering workflows from external environments. API functionality can be further enhanced by pairing it with MivaScript modules.

Last but not least, Miva gives developers full front-end file system access via SFTP and supports Git workflows for proper version control and deployment. Simply put, every theme file, template, resource, or module output can be edited directly, meaning your teams are handed complete visibility and control over the codebase!
Scalability (Shopify wins)
The Verdict: Even though Miva Merchant offers a far wider range of customization options, Shopify still wins. That's because Shopify’s architecture is designed to support the scalability needs of businesses of all sizes, even small startups.
Miva Merchant, on the other hand, is engineered mostly for enterprise-level environments, where teams have the capacity to manage servers and write backend logic. Let's have a clearer look at the difference between Miva Merchant vs Shopify below:
Shopify’s scalability
Since its release, Shopify has been purpose-built to scale effortlessly, thanks to its fully managed cloud infrastructure.
Indeed, merchants don’t have to configure servers, manage performance, optimize speed, or handle security patches; Shopify’s system does all of that automatically. Plus, since Shopify is fully hosted with automatic scaling, the platform absorbs traffic increases without requiring merchants to upgrade servers or reconfigure anything behind the scenes.
We also observe that its global CDN and 99.99% uptime ensure fast loading times, even as the audience grows across multiple markets. Likewise, stores can expand product catalogs indefinitely, relying on Shopify’s infrastructure to accommodate large SKU counts and high order volumes without replatforming.
And don't forget that operational-wise, Shopify is equally scalable. As discussed earlier, its API suite, Shopify Functions, and automation tools allow mid-sized and enterprise merchants to integrate ERPs, WMS, CRM, OMS, and other operational systems without custom server logic. The app ecosystem further minimizes development work by providing ready-made solutions for most business needs.
This is why Shopify is often described as “scalable by default”: a small merchant can begin with a simple store and evolve into a multi-market enterprise operation using the same underlying system.
Miva Merchant’s scalability
Though Miva Merchant is also highly capable of scaling, its approach is very different and suited only to businesses with significant technical resources.
Unlike Shopify, Miva requires merchants or developers to manage server installation and systems maintenance, which creates an immediate barrier for small and mid-sized businesses that cannot justify DevOps overhead.
Additional capabilities (such as Miva’s hooks, events, Morph technology, and JSON API combined with backend modules) allow enterprises to create advanced ERP, WMS, and OMS integrations. However, these integrations typically require far more development work than Shopify’s plug-and-play app ecosystem. Furthermore, Miva’s open file system access through SFTP and Git workflows gives developers complete control but shifts responsibility for deployments and versioning entirely to the merchant’s team.
In short, for enterprise companies with in-house developers who need to engineer their ecommerce environment with precise control, these features are a strength. But for small, medium, and even many large merchants, this level of technical complexity becomes unnecessary overhead.
SEO & Marketing (Miva Merchant wins)
The Verdict: Both Shopify and Miva Merchant offer strong marketing capabilities. But when it comes to SEO, Miva offers more advanced and open-ended SEO configurations.
This distinction between Miva Merchant vs Shopify becomes easier to see once we explore how each platform approaches marketing and search optimization in practice:
Shopify’s SEO & marketing
From our observation, Shopify takes a comprehensive and user-friendly approach to marketing by centralizing most tools within the dashboard. Its Marketing Hub allows merchants to run campaigns, track conversions, and evaluate performance across digital channels without leaving the administrative interface.
The system also breaks down where traffic originates, how each campaign converts, and how promotions (such as discount codes, BOGO deals, or automated offers) contribute to overall revenue. Better yet, Shopify’s native integrations with platforms like Facebook, Instagram, TikTok, Google, and Pinterest further support multi-channel marketing, allowing your team to coordinate campaigns from a single environment.
On another note, Shopify’s SEO foundation is simple but overall well-executed. It automatically manages canonical tags, sitemaps, robots.txt, SSL certificates, and social metadata, meaning merchants are provided with a strong baseline as soon as the store goes live. The platform also allows editing of meta titles, descriptions, URLs, alt text, and redirect structures, enabling fine-tuning for individual pages.
Miva Merchant’s SEO & marketing
From a marketing perspective, Miva Merchant keeps pace with Shopify by offering a wide, well-structured set of built-in tools.
Its promotions framework centers on Price Groups, which determine discount logic, eligibility rules, tiered pricing, bundles, and BOGO configurations. Coupons, whether generated individually or in bulk, are paired with Price Groups to define exactly how and when discounts apply.
Miva also includes native gift certificate management, allowing merchants to create codes, sell certificates as products, and configure automated delivery emails. Upsell and cross-sell items can be tied to product pages or checkout flows, and the affiliate system enables straightforward management and tracking of payouts.
Furthermore, SEO is where Miva distinguishes itself most clearly:
- Its admin tools allow merchants to edit meta titles, descriptions, and meta robots tags for products, categories, and key site pages.
- Miva’s URI Management provides comprehensive control over URL structures, enabling merchants to define patterns for product, category, and general pages.
- The platform also supports native 301 redirects (either individually or imported in bulk), making it easier to manage permalink changes or migration scenarios without reliance on server-level files.
And that's not all; beyond these features, developers can configure canonical URLs directly within templates, giving fine-grained control over duplicate content. Structured data for Product, Offer, Organization, WebSite, and Reviews can be added directly within templates to support rich snippet eligibility. We also found that pagination markup and faceted navigation strategies can be implemented with developer guidance, so that you can ensure large catalogs avoid index bloat and maintain clean search structures.
Of course, these advanced options still require some custom work, but this technical nature is precisely what gives Miva an edge. For businesses with the resources to take advantage of it, the platform’s openness enables deeper, more advanced SEO optimization than Shopify currently allows.
Apps and Integrations (Shopify wins)
The Verdict: Shopify's ecosystem is vast, well-established, and designed to give merchants instant access to thousands of tools that expand their store’s functionality with almost no effort. Miva Merchant, by contrast, offers only a small selection of modules.
Sure, Miva does allow developers to integrate external services through custom work. Nevertheless, the sheer convenience, speed, and breadth of Shopify’s App Store make it far more practical for most merchants. Let's look at the differences between Miva Merchant vs Shopify more closely:
Shopify’s apps & integrations
It's clear that Shopify has built one of the most extensive integration ecosystems in the eCommerce world. Its dedicated App Store features more than 13,000 apps spanning every category a merchant might need, including SEO improvements, personalized email automation, advanced analytics dashboards, subscription management, loyalty programs, upsell engines, and more!
Furthermore, what makes Shopify’s ecosystem particularly effective is how seamless and intuitive the installation process is. Merchants can browse categories, evaluate apps based on detailed reviews and ratings, compare transparent pricing, and install them with a single click. Better yet, many apps offer free trials or affordable entry-level plans, typically between $5 and $20 per month, meaning they are easily accessible to both smaller merchants and larger operations.
Miva Merchant’s apps & integrations
On the other hand, Miva Merchant's ecosystem is dramatically more limited, with only around 16 apps.

Sure, many of these are free, and the paid modules are reasonably priced (generally between $50 and $100). Nevertheless, the small selection means merchants have far fewer options for enhancing their store without custom work.
Even worse, another critical drawback is the near-total absence of ratings or user reviews for these modules. Without feedback or usage history, merchants cannot easily judge the app's reliability, performance, or quality. The only way to evaluate these criteria is to download and test the app directly, which not only slows down your decision-making process but also introduces unnecessary risk.
Customer Support (Miva Merchant wins)
The Verdict: Miva Merchant offers direct human assistance alongside comprehensive self-service materials, creating a support system that feels both accessible and dependable.
Shopify, on the other hand, has steadily shifted toward a largely self-service model, as seen in our Miva Merchant vs Shopify breakdown below:
Shopify’s customer support
Shopify relies on a corporate, streamlined system that prioritizes documentation and self-help resources over live interaction.
Specifically, when merchants need assistance, they are typically directed to complete an online form, after which Shopify follows up by email. This pathway is mostly applicable for pre-sales inquiries, when potential customers are gathering information.
Unfortunately, once a store is up and running, securing direct, individualized support becomes far more challenging.
Since Shopify has removed phone support entirely, merchants are instead guided toward the Help Center, FAQs, and the Shopify Community Forums. Sure, these resources are extensive and well-organized, but they also remove the personal element. Users must sift through articles, interpret solutions, and troubleshoot on their own, which is quite stressful and time-consuming when urgent or complex issues arise.
Miva Merchant’s customer support
Unlike Shopify, Miva provides direct human support as a standard part of the merchant experience.
Users can submit tickets through the support portal and receive responses directly from the Miva team. Not to mention, since store setup, pricing inquiries, and technical onboarding all require initial contact, that means merchants receive personalized assistance from the moment they begin working with the platform!
In addition to traditional support, Miva also offers a Wishlist Request channel where merchants can request new features directly from the Miva Merchant Development Team. Better yet, the platform complements its human support with a wide collection of self-help resources, including:
- The community forum, which allows users to exchange ideas and troubleshoot together,
- Video tutorials, documentation, and extensive developer materials, which cover everything from basic setups to advanced API usage.
Together, these resources create a support environment that is not only comprehensive but also highly approachable. Compared to Shopify’s increasingly hands-off system, Miva’s assistance and in-depth educational content make it feel far more merchant-focused and responsive.
Security (Shopify wins)
The Verdict: Shopify offers stronger overall security for most merchants due to its fully managed infrastructure, automatic updates, and standardized advanced security features. Its large engineering resources and centralized monitoring give it a significant advantage in preventing and responding to threats.
Miva Merchant is also secure, but it shines best when paired with technical expertise. Let's have a closer look at this Miva Merchant vs Shopify difference:
Shopify security
Shopify operates as a fully hosted SaaS platform, which means it manages the entire security stack for you, from server infrastructure and firewalls to ongoing monitoring and threat detection. The platform is PCI DSS Level 1 compliant, and every store automatically receives an SSL certificate, ensuring that payment data and customer information are always encrypted in transit.
And that's not all. Shopify also offers several advanced security features that are standardized across its ecosystem. These include two-factor authentication for admin users, detailed staff permission controls, and activity logging to track changes within the store.
The only trade-off is that Shopify’s large app ecosystem introduces a broader surface area for third-party risk. Hence, merchants must choose reputable apps and review permissions carefully.
Miva merchant security
Like Shopify, Miva Merchant also provides strong foundational security, including PCI DSS compliance and support for SSL encryption. The platform emphasizes security within its architecture and delivers regular patches, updates, and server-level protections.
Because Miva’s ecosystem is smaller and more controlled, the platform naturally carries less third-party extension risk compared to Shopify. Still, the security setup usually depends more heavily on the merchant’s developers or hosting environment, which may require closer oversight to maintain best-practice security standards.
Pricing (Shopify wins)
The Verdict: Shopify's plans are affordable, transparent, and easy to understand, giving merchants a predictable cost structure from day one. Miva Merchant, on the other hand, tends to be more expensive and does not provide standardized pricing tiers.
In short, for most businesses (especially small and mid-sized ones), Shopify’s clarity and accessibility make it the more attractive option.
This Miva Merchant vs Shopify contrast becomes even more apparent when we look at how each platform structures its pricing model.
Shopify’s pricing
Shopify offers four clearly defined plans, each tailored to a specific level of operational complexity:
- The Basic plan, at $39 per month, includes all the essentials for running a small business. Merchants can manage up to 10 inventory locations, receive 24/7 chat support, and sell in person using a phone or POS device.
- The Grow plan (formerly known as “Shopify”), priced at $105 per month, builds on the features of Basic. Merchants receive five staff accounts, maintain access to 10 inventory locations, and continue to benefit from round-the-clock support.
- For brands preparing to scale, the Advanced plan offers even more capability at $399 per month. It includes localized storefronts by market, enhanced analytics, 15 staff accounts, and the same 10 inventory locations.
- Finally, Shopify Plus represents the enterprise-level offering, starting at around $2,300 per month. This plan provides unlimited staff accounts, fully customizable checkout, wholesale and B2B selling features, priority 24/7 phone support, and the ability to manage up to 200 POS Pro locations.
Miva Merchant’s pricing
Miva Merchant once offered public pricing plans, but that structure no longer exists.
Instead, merchants must contact the Miva team directly to receive a personalized quote. During this process, Miva asks prospective customers to identify their annual online revenue as:
- Under $1 million
- Between $1 million and $5 million
- Or $5 million and up.
From there, the sales team evaluates the business’s needs and provides a tailored price.
Since pricing is not published and varies from store to store, merchants do not get the same clear-cut cost expectations that Shopify provides. However, based on industry research and user reports, we can say Miva’s pricing typically ranges from roughly $100 to $600 per month, depending on the features, modules, and level of support a business requires.
Our Methodology: How We Test Miva Merchant vs Shopify
Step 1: Establishing the comparison framework
To make sure this Miva Merchant vs Shopify analysis provided practical findings, we started by defining a clear evaluation framework and selected key eCommerce areas that meaningfully influence real merchant workflows. Then, for each platform, we created three merchant profiles to guide the testing process:
- One profile represented a new seller building their first store with no technical experience.
- Another reflected a mid-sized retailer managing a large catalog and relying on third-party tools to automate operations.
- The final profile modeled an enterprise business that depends on custom backend logic, structured integrations, and developer-led workflows.
Step 2: Direct platform testing and scenario replication
Both platforms were then tested hands-on as we created new stores and walked through the full setup workflow. This included:
- Onboarding
- Theme configuration
- Product creation
- Payment setup
- Shipping rules
- App installation
- Analytics testing
- Running simulated checkouts.
After the foundational setup, we recreated more complex operational scenarios, such as large catalog imports and customization experiments at both template and backend levels. Both platforms were used repeatedly over several weeks to ensure our assessment reflects long-term usability rather than first impressions.
Step 3: Weighting categories and scoring performance
Once testing was complete, we assigned weighted values to each evaluation category based on how strongly it affects a merchant’s success in 2025. The percentages reflect the practical impact each area has on real ecommerce operations:
- Ease of use – 15%
- Customization flexibility – 15%
- Apps & integrations – 15%
- Inventory management – 10%
- Payments – 10%
- Shipping – 10%
- SEO & marketing – 10%
- Scalability & performance – 10%
- Customer support – 3%
- Security – 2%
Weighting the categories in this way allowed the final verdict to reflect not just how powerful the platforms are on paper, but how well they deliver for real merchants operating at different stages of growth.
Miva Merchant vs Shopify: FAQs
How does Miva compare to Shopify?
Miva offers deep customization and control, ideal for complex, established businesses. However, it has a steeper learning curve and a smaller app ecosystem. Shopify is simpler, more user-friendly, and scalable for most businesses, with a massive app store and lower entry cost, though less control over core code.
How does Miva handle payments?
Miva handles payments primarily through its native solution called MivaPay, which is powered by PayPal. Merchants can also integrate a wide range of other third-party payment gateways and services.
Who is Shopify’s biggest competitor?
Shopify's biggest competitors include BigCommerce (strong built-in features for scaling businesses), WooCommerce (for WordPress users needing deep customization), Adobe Commerce (Magento) (enterprise-level control), and Salesforce Commerce Cloud (large enterprise focus).
Which site is better than Shopify?
The best alternative depends on your needs. BigCommerce is great for large-scale growth (no transaction fees); WooCommerce ideal for full WordPress control; Wix is perfect for beginners needing easy design; and Squarespace is best for creatives focused on aesthetics.
Final Words: Which One to Choose?
So, between Miva Merchant vs Shopify, which one is better?
All in all, Miva Merchant is best suited for enterprise-level businesses or mid-sized brands with complex requirements, internal development teams, and a clear need for advanced catalog structures or backend logic.
On the other hand, Shopify is the stronger choice for businesses that prioritize ease of use, scalability, and operational efficiency. It is especially ideal for small and mid-sized businesses that need predictable pricing and fast deployment without technical overhead.
In short, the right choice depends on your business model:
- Choose Miva if you need engineering-level flexibility
- Choose Shopify if you want a platform that grows with you effortlessly and requires far less upkeep.

