A Point of Sale (POS) system is more than just a payment processor. It’s a key tool that helps businesses, from small shops to large restaurants, operate smoothly and grow. Whether you're a business owner or IT professional, understanding how does a POS system work is essential for making the right choice.
POS systems have come a long way from being simple cash registers. Today’s solutions are capable of boosting customer satisfaction, helping with business insights, and saving time.
In this article, LitExtension will explore:
- What is a POS system;
- How does a POS system work;
- The key components of a POS system;
- How you can use its full potential to enhance your business operations.
What is a POS System?
Before discussing the question, “How does a POS system work?”, let’s see what a POS system is in the first place.
At its core, a POS system is a combination of hardware and software that allows businesses to handle customer transactions. But in practice, it does so much more. It integrates various aspects of business operations, including inventory management, customer relationship management (CRM), and sales tracking, into one streamlined solution. This ensures that each sale is not only processed quickly but also that critical business data is updated in real time.

For a retail or hospitality business, a POS system might include both physical hardware (like a terminal and receipt printer) and software that tracks inventory, processes payments, and generates reports. It’s what ensures that every time a customer buys a product or service, the sale is recorded, inventory is updated, and all financial records are in sync with your accounting system.
In practical terms, a POS system functions as the central nervous system of your business. It can:
- Process sales: When a customer purchases, the POS system records the sale, calculates the price, taxes, and discounts, and processes the payment.
- Manage inventory: As items are sold, the system automatically updates inventory levels, helping you keep track of stock without manual counting.
- Generate reports: POS systems provide real-time sales data, allowing you to monitor performance, identify trends, and make informed decisions.
- Enhance customer relationships: Many POS systems come with built-in CRM tools, helping you track customer preferences, purchase history, and even manage loyalty programs.
In short, a POS system can be the key to running a more efficient and profitable business, especially when you understand its full potential.
How Does a POS System Work?
A POS system, at its core, logs customer purchases, processes payments, and issues receipts, either through printing or by sending them electronically via text or email. Additionally, many top POS systems for small businesses offer features like report generation, inventory management, and employee time tracking, enhancing overall efficiency.
Let’s break down how a POS system works in everyday business situations, from the moment a customer walks up to your checkout counter to the moment you run sales reports at the end of the day. Each step happens seamlessly, in just seconds, ensuring that both the customer and the business experience a smooth transaction.
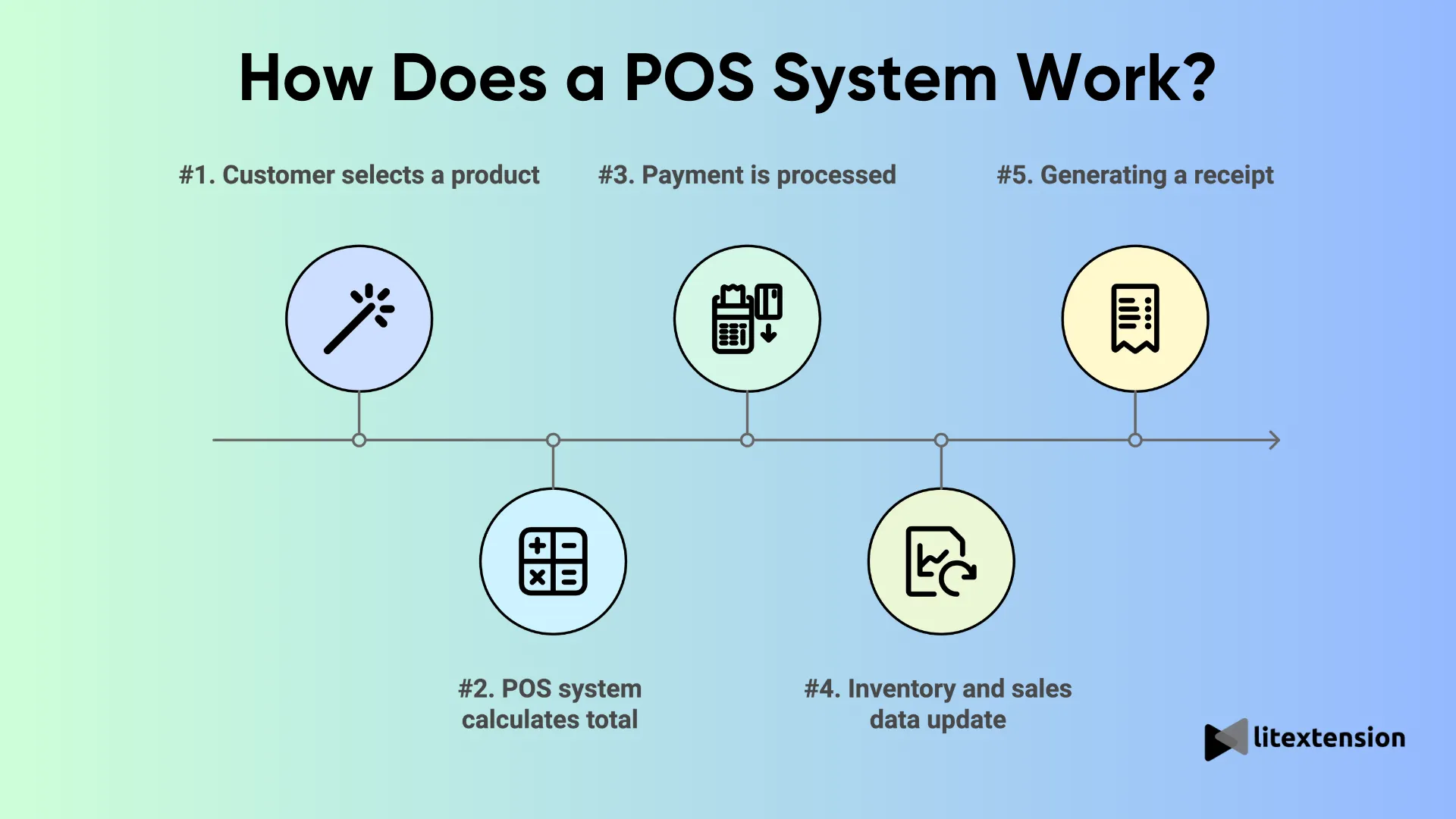
1. Customer selects a product
The first step happens when the customer decides to buy something. Whether they’re adding an item to their online shopping cart or bringing a product to your store’s checkout counter, this action triggers the POS system to start the sales process.
2. The POS system calculates the total
Once the product is selected, the POS system does the heavy lifting. It calculates the total cost of the item(s), including any taxes, discounts, or promotions. If you’re running a restaurant, it might also calculate tips and split checks, depending on what the customer chooses.
3. Payment is processed
Next, the POS system processes the payment. This could be cash, credit/debit card, or even mobile payment options like Apple Pay or Google Pay. Modern POS systems integrate seamlessly with payment gateways, ensuring secure and fast processing. If the payment is successful, the system marks the transaction as complete.
4. Inventory and sales data update
After the transaction, the POS system automatically updates your inventory to reflect the items sold. This is critical for keeping track of stock levels and ensuring you’re not overselling products that aren’t available. Simultaneously, it logs the sale data, making it available for real-time reporting.
5. Generating a receipt
Finally, the system generates a receipt, either printed or sent electronically, to confirm the purchase for the customer. This step completes the transaction on the customer’s end, but for the business, it means all related data, sales figures, tax calculations, and inventory levels, is updated in the background.
Benefits of a POS system
Now that we have answered the question, “How does a POS system work?”, let’s move on to its benefits.
All in all, adopting a modern point-of-sale (POS) system can do far more than simply replace an old cash register. When implemented effectively, it can become the operational backbone of your retail business, helping you serve customers faster and make decisions grounded in reliable data:
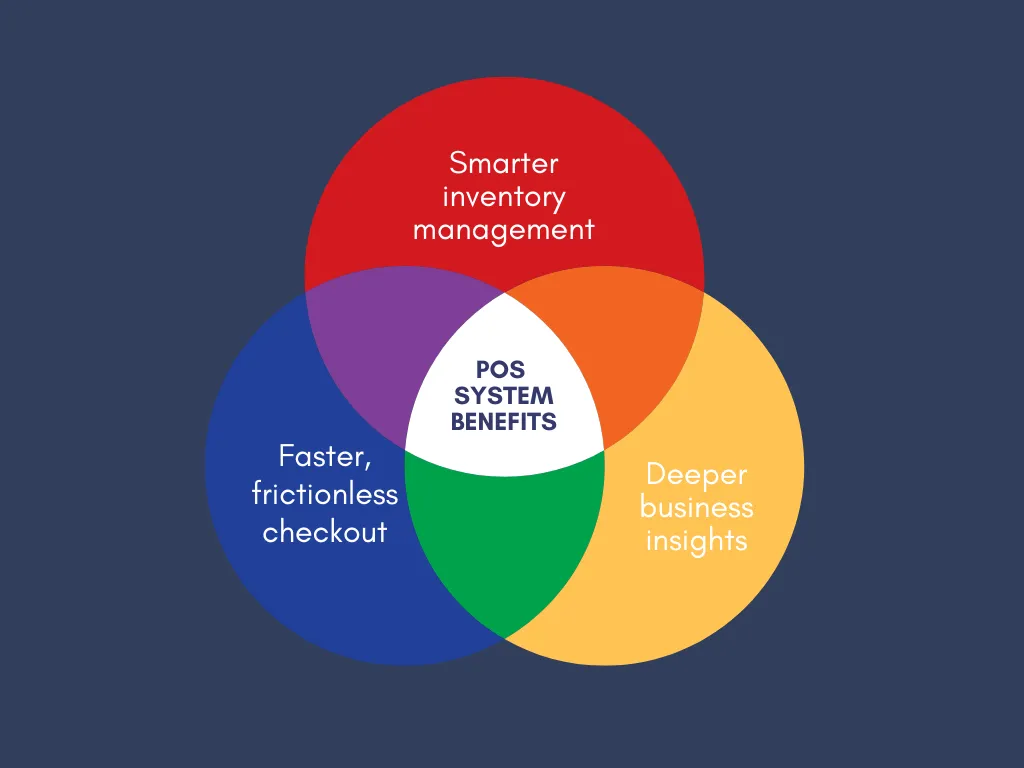
Smarter inventory management
For most retailers, inventory is both the biggest asset and the biggest operational challenge. Without accurate, up-to-date stock data, it’s easy to run into costly issues, such as overselling items you don’t have or tying up capital in slow-moving products!
Fortunately, a modern POS system with built-in inventory management tools solves this problem by giving you real-time visibility into every product in your catalog.
Instead of juggling spreadsheets or performing manual counts that take hours, you can add products individually or in bulk and track stock levels automatically. Many advanced POS systems also let you set reorder points, so the system can alert you (or even prepare purchase orders) when popular items are running low.
Faster, frictionless checkout
Inventory aside, remember that the checkout experience is often the last interaction a customer has with your store, which makes it a critical moment for leaving a positive impression.
And from our observation, a well-optimized POS system can dramatically reduce waiting times by processing transactions quickly and accurately. For customers, this means a smoother, less stressful shopping experience. For staff, it means fewer technical issues and more time to engage with shoppers on a personal level.
In addition, speed is especially important during peak hours or seasonal sales. With a responsive POS system, staff can scan items, process payments, and complete transactions in a fraction of the time it would take with older equipment. Some systems even allow for mobile or tablet-based checkouts, so sales associates can assist customers anywhere in the store instead of making them wait at a fixed counter.
Deeper business insights
Lastly, today’s leading POS systems go beyond transaction recording; they act as powerful analytics tools that reveal patterns in sales, inventory, staffing, and customer behavior. This built-in reporting capability allows business owners to make smarter, data-driven decisions instead of relying on guesswork.
For example, by analyzing sales reports, you can identify top-selling products, seasonal demand trends, and underperforming items that may need to be discounted or phased out. Plus, staffing reports can help you match employee schedules to peak shopping hours, ensuring the right level of service without overspending on labor costs.
Besides, customer data collected through the POS can also be integrated with marketing tools, enabling targeted campaigns based on purchase history, preferences, and engagement. Simply put, having accurate data at your fingertips makes it easier to nurture long-term relationships and drive repeat sales.
What Are the Key Components of a POS System?
To fully understand how does a POS system work, it’s essential to know the two key components that make up the system: hardware and software. Both are equally important and work together to process transactions, manage sales, and handle many other business tasks. Depending on your business needs, the combination of these components can vary.
Let's see what each of these components includes and how they contribute to the overall system.
1. POS hardware
POS hardware refers to the physical devices you’ll need to process sales and manage transactions in-store. These devices can range from traditional desktop setups to sleek, mobile POS systems used in restaurants or pop-up shops.
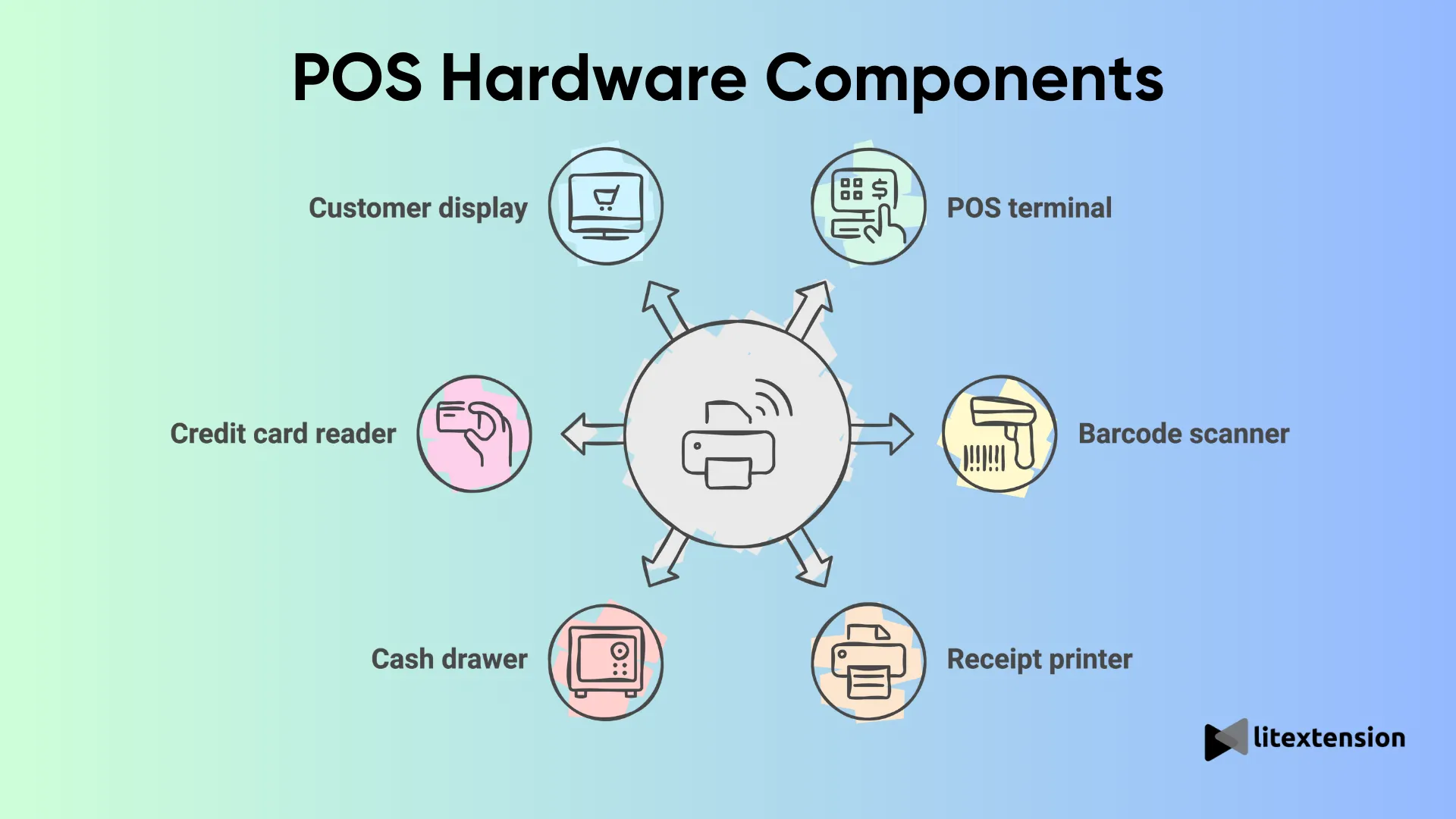
- POS terminal: This is the brain of the operation, where all transactions are processed. It’s often a computer or a tablet where sales associates or servers enter product information and process payments.
- Barcode scanner: In retail, a barcode scanner makes ringing up items quick and error-free. It scans product barcodes, instantly pulls up prices, and updates the inventory as items are sold.
- Receipt printer: Once the transaction is complete, most POS systems are connected to a receipt printer that provides customers with proof of purchase. However, many businesses are moving toward email or digital receipts as an environmentally friendly alternative.
- Cash drawer: Even though digital payments are becoming more popular, many businesses still handle cash transactions. A cash drawer connected to the POS terminal allows businesses to store cash while syncing sales information with the system securely.
- Credit card reader: With the rise of contactless payments and chip-enabled cards, most POS systems now require a modern credit card reader that accepts swipes, taps, and chip transactions.
- Customer display: Some systems include a customer-facing screen that allows shoppers to view their purchase details before confirming the transaction. This is especially helpful in restaurants and cafes.
FYI: For businesses that need flexibility, mobile POS (mPOS) or tablet POS systems are becoming increasingly popular. These systems allow you to process sales anywhere within your store, or even outside it. Restaurants use tablet POS systems to allow waiters to take orders directly at the table, while retail shops might use mobile POS setups to process sales at pop-up events.
2. POS software
If hardware is the backbone of your POS system, then software is the heart. The software allows the system to process sales, manage inventory, track employee performance, and much more. There are different types of POS software, depending on the needs of your business.
- Sales tracking: At its most basic, POS software tracks all sales made through the system. This data can be used for real-time reporting, allowing you to monitor sales performance and identify trends.
- Inventory management: Modern POS systems often come with inventory management tools that automatically update stock levels as sales are made. This can prevent overselling and help ensure you always have popular items in stock.
- Customer relationship management (CRM): Many POS systems include built-in CRM features, allowing you to keep track of customer data, including purchase history and preferences. This helps businesses personalize customer interactions and manage loyalty programs.
- Employee management: Managing staff becomes easier with POS software that tracks employee performance, handles shift scheduling, and even helps with payroll integration.
- Reporting and analytics: POS software provides real-time reports on sales, inventory, and employee performance. These reports are essential for making data-driven decisions to improve your business.
- Multichannel integration: For businesses with both physical stores and online shops, many POS systems offer multichannel integration, allowing you to manage both online and offline sales from one platform.
3. Payment processing
A vital function of any POS system is processing payments. Payment processing is the mechanism that allows you to accept and manage various types of payments, including cash, credit/debit cards, and mobile payments.
Most POS systems are integrated with payment gateways to handle these transactions. Here’s how the payment processing generally works:
- Card payment: When a customer swipes, taps, or inserts their card into the credit card reader, the POS system sends the payment information to a payment processor. The processor then communicates with the bank to authorize the payment.
- Mobile payments: Many POS systems now support mobile payment options like Apple Pay or Google Pay, making transactions fast and secure.
- Transaction security: A big part of payment processing is ensuring the security of each transaction. Most POS systems use encryption and tokenization to protect sensitive payment data and comply with PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards).
In sum, your POS system’s hardware and software work together to ensure every transaction is fast, secure, and seamless.
Types of POS Systems
As we did know how does a POS system work, let's learn about the types of POS systems. There are different types out there to suit the needs of businesses of all sizes, industries, and sales volumes. Let’s dive into some of the most common ones and see what makes each unique.
Traditional POS vs Cloud-based POS
Traditional POS systems store all their data on a local terminal or the company’s own server. Back in the day, these were mostly installed on desktop computers and needed regular updates and maintenance. They’re a stable option for larger businesses with high sales, but they can be expensive to maintain and upgrade.
On the other hand, cloud-based POS systems are hosted online, so you can access sales data, inventory, and reports from anywhere. This flexibility makes them ideal for small businesses or companies with multiple locations. Plus, they’re more scalable and usually cheaper to maintain, since updates happen automatically.
Mobile POS (mPOS) vs ePOS
If portability is important for your business, think of food trucks, pop-up shops, or tight spaces. MPOS systems are a great fit. These typically run on tablets or smartphones, allowing you to move around while still managing inventory, tracking sales, and processing payments.
Similar to traditional systems, ePOS uses digital tools and cloud-based software to handle transactions. It's especially popular for businesses that want to manage both online and in-store sales in one place, offering multichannel capabilities.
Industry-specific POS solutions
Some POS systems are tailored to specific industries. Here are a few examples:
- Retail POS: Perfect for stores selling physical goods, with features like inventory management, sales tracking, and loyalty programs.
- Restaurant POS: Designed for food and beverage businesses, offering table management, tip calculation, and the ability to split checks.
- Service-based business POS: Ideal for salons or repair services, these systems focus on appointment scheduling, customer relationship management (CRM), and tracking services provided.
How Much Does A POS System Cost?
When calculating the total cost of a point-of-sale (POS) system, there are three primary factors to consider: the hardware required to run it, the software that drives its functionality, and the ongoing fees for processing payments.
POS hardware expenses
Your hardware investment will largely depend on how simple or advanced your POS setup needs to be.
Specifically, for small businesses, mobile vendors, or pop-up shops, a basic smartphone paired with a card reader can be all that’s necessary. Entry-level magstripe readers are sometimes free with account sign-up, while more advanced chip-and-contactless models typically cost between $20 and $60.
However, as your operations grow, so do your hardware requirements.
Businesses that need greater functionality may opt for mobile POS terminals that combine card acceptance, barcode scanning, and receipt printing in one unit, usually priced between $240 and $630. And at the higher end, a complete countertop register system (which might include both customer-facing and staff-facing screens, a cash drawer, card reader, and receipt printer) can range from $1,200 to $1,800.
POS software fees
Once your hardware is in place, software becomes the engine that powers your POS system. Pricing here can vary widely depending on the features you need.
Most providers offer tiered plans, starting at no cost for basic setups and climbing to around $400 per month for comprehensive packages. If you want to add specialized capabilities (such as loyalty programs, marketing automation, or online ordering), these are often sold as add-ons, generally costing between $10 and $100 per month. Restaurant-focused solutions tend to fall on the higher end due to the complexity of their operations.
Payment processing charges
Beyond hardware and software, payment processing fees form the third major component of POS costs. These charges are applied to every card transaction, typically amounting to 1.5% to 3.5% of the total sale, plus a small fixed fee in some cases.
The exact rate you pay depends on your processor’s pricing model and the type of transaction. In-person purchases usually have lower fees than online or card-not-present payments. On top of this, some providers may also impose additional costs like chargeback fees or PCI compliance charges, so it’s important to factor these into your overall budget.
POS System Integrations with Other Business Tools
One of the best things about modern POS systems is how easily they can connect with other important business tools. Whether you're handling accounting, running an eCommerce store, or managing a large enterprise, a well-integrated POS system can make your operations smoother by automating tasks and keeping everything in sync across platforms. Understanding how does a POS system work with other systems is key to optimizing your business.
1. POS and eCommerce integration
If you run both a physical store and an online shop, having a POS system that integrates with your eCommerce platform is a must. Many cloud-based POS systems can sync with popular eCommerce platforms like Shopify POS, WooCommerce, or Magento, allowing you to manage both your online and in-store sales in one place.
Here’s why this integration is so useful:
- Your stock levels are updated in real-time across both online and in-store sales, so you don’t have to worry about overselling products.
- Whether a customer buys online or in-store, their purchase history is stored in one system. This makes it easier to run personalized marketing campaigns and manage loyalty programs.
- You can easily track and manage orders across all channels, making it simple to fulfill online orders from your physical store or the other way around.
Integrating your POS with your eCommerce platform will ensure a seamless multichannel experience for your customers while making things simpler for your team.
2. POS and accounting software integration
If you’ve ever had to manually enter sales data into your accounting software, you know how time-consuming and error-prone it can be. That’s where POS and accounting software integration really shines. Many modern POS systems, especially cloud-based ones, work seamlessly with popular accounting platforms like QuickBooks or Xero.
By linking your POS with your accounting software, you can automatically sync sales data, tax info, and expenses, which helps reduce the chance of mistakes. Here's why this is helpful:
- Every transaction in your POS gets automatically updated in your accounting system.
- Sales tax is calculated and recorded, making tax season way less stressful.
- Real-time integration means more accurate and up-to-date financial reports.
For IT teams, setting up these integrations is often done via APIs or pre-built connections. For business owners, it means smoother day-to-day operations and fewer accounting headaches.
3. POS and ERP integration
If you’re running a larger business or planning to scale up, integrating your POS system with an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system can be a game-changer. ERP systems manage multiple aspects of your business, like inventory, supply chains, HR, and finance. When your POS and ERP systems are synced, everything works together more efficiently, and you get a clearer picture of your business’s overall performance.
Here’s how this integration can benefit you:
- Your POS updates stock levels in the ERP system in real time, smoothing supply chain management.
- With both POS and ERP data in one place, you can generate detailed reports on sales trends, employee performance, and more.
- Syncing POS and ERP systems lets you track orders from the point of sale all the way through to fulfillment, ensuring smoother customer experiences.
This integration is essential for scaling up efficiently for growing businesses, especially in industries like retail and hospitality.
How Does a POS System Work: FAQs
What is a POS transaction?
A POS transaction is any sale that occurs at the point of sale, whether it’s in a physical store, online, or through a mobile device. It typically involves a customer selecting a product or service, paying for it, and receiving a receipt.
What is the difference between a POS system and a cash register?
While both systems handle payments, a POS system offers much more functionality than a traditional cash register. A POS system can track sales, manage inventory, handle customer data, and generate detailed reports, while a cash register is limited to basic transaction processing.
How does a POS system work step by step?
A POS system processes transactions in a few simple steps:
1. Product selection: The customer chooses an item or service.
2. Price calculation: The POS system totals the price, including taxes and discounts.
3. Payment processing: The customer pays using cash, card, or mobile payments.
4. Inventory update: The system adjusts stock levels for the purchased items.
5. Receipt generation: A receipt is printed or sent electronically, completing the transaction..
How does a POS machine work technically?
Technically, a POS machine connects to various components such as barcode scanners, card readers, and printers. It communicates with payment gateways to process credit or debit card transactions, securely sending payment information to banks for approval. The machine’s software processes the sale, updates inventory, and generates reports. Data is often stored in the cloud or on a local server.
How does a POS account work?
A POS account is a bank account where businesses receive payments from sales processed through the POS system. When a customer makes a payment via card, the funds are transferred to the business’s POS account after being cleared by the payment processor, typically within a few business days.
How do you use POS for the first time?
To use a POS for the first time, you first install and set up the hardware and software, integrate it with your inventory and payment systems, and input your products. Then, you should train your staff to operate the system, process test transactions, and ensure everything works smoothly before going live with customers.
Final Words
In summary, understanding how does a POS system work is essential to streamline operations and enhance customer service. A POS system processes sales, manages inventory, and tracks customer data all in one platform, making day-to-day operations more efficient. Every step happens seamlessly in real-time, from selecting products and processing payments to updating inventory and generating reports. With the right system in place, your business can boost productivity, reduce errors, and improve the overall customer experience, whether you're running a small shop or a large-scale operation.
We hope you found this information helpful! If you'd like to learn more, visit our eCommerce blog for in-depth articles and tips. Also, don’t forget to join our Facebook community to connect with other business owners and stay updated on the latest trends.

