B2B sales are no longer about relying on a single channel and hoping it scales. As buying behaviors evolve and decision-making becomes more complex, teams now have more sales channels to choose from than ever before. The challenge is no longer access – it’s knowing which B2B sales channels actually fit your business.
In this article, we break down the most effective B2B sales channels and explain how they work in practice:
- Direct sales channels;
- Indirect/partner sales channels;
- Marketing and digital sales channels;
- Events and relationship-based channels.
Let’s get started!
What are B2B Sales Channels?
B2B sales channels refer to the ways businesses sell products or services to other businesses, from first contact to final deal closure. Unlike B2C sales, B2B selling usually involves longer decision cycles, multiple stakeholders, and higher deal values. It is less about quick transactions and more about building trust, proving long-term value, and managing relationships over time.
To help you avoid confusion, we have outlined the differences between B2B vs B2C vs distribution channels. While these concepts often overlap in practice, they serve different purposes in how products are marketed, sold, and delivered.
Field | B2B | B2C | Distribution |
Buyer type | Businesses, organizations, or enterprises | Individual consumers | Retailers, wholesalers, resellers, or marketplaces |
Sales cycle length | Long and multi-stage, often weeks or months | Short and transactional | Not sales-focused; depends on supply chain flow |
Decision makers | Multiple stakeholders (procurement, managers, executives) | Single buyer or household | Business partners, distributors, or logistics teams |
Deal size | High-value contracts or recurring subscriptions | Low to mid-value individual purchases | Focused on volume rather than deal value |
Relationship depth | Deep, long-term, and relationship-driven | Shallow to moderate, often transactional | Operational and contractual rather than relational |
Common channels | Direct sales, events, webinars, referrals, professional networks | Ads, social media, eCommerce stores, influencers | Wholesalers, distributors, retail partners, fulfillment networks |
Below, we break B2B sales channels into several practical groups, each suited to different sales motions and buyer expectations. Keep reading to explore the top sales channels for generating B2B leads!
Direct Sales Channels
Within B2B sales channels, direct sales channels give businesses full control over the customer relationship and the transaction. In practice, this group includes several approaches that are widely adopted today and consistently deliver results across different B2B models.
1. In-house sales team
An in-house sales team gives companies direct control over how prospects are qualified, educated, and converted. In B2B environments, this level of control becomes increasingly important as sales cycles grow longer and buying decisions involve multiple stakeholders.

In recent years, the role of internal sales has remained largely the same, but day-to-day execution has changed. Sales reps now work with CRM data, buyer intent signals, and marketing insights to guide conversations. As a result, teams can prioritize higher-quality opportunities and engage buyers in a more consultative manner throughout the sales process.
Pros | Cons |
|
|
Best for: Enterprise software, industrial products, and consultative B2B services.
2. Outbound sales
Outbound sales proactively generate opportunities by engaging prospects before they enter a traditional buying cycle. Rather than waiting for inbound interest, this approach allows B2B teams to actively reach the right accounts and shape the buying conversation from the start.
The modern shift in outbound is moving away from “volume” toward precision. Success now depends on relevance: identifying the right stakeholder, understanding their specific pain points, and timing the outreach to match their business needs. When executed with this consultative mindset, outbound ceases to be a “push” tactic and instead becomes a way to initiate high-level, strategic partnerships.
Pros | Cons |
|
|
Best for: B2B companies targeting specific accounts or niches where demand needs to be created rather than captured.
3. B2B eCommerce site
As digital buying becomes the industry standard, a company-owned B2B eCommerce site serves as a 24/7 digital storefront. Buyers can place orders, view pricing, and manage accounts through a self-service experience that fits their own pace. This setup streamlines repeat purchases and allows sales teams to focus on more complex, high-value opportunities.
According to DynamicWeb’s 2025 B2B eCommerce report, 85% of B2B companies already run an online portal, with many expecting 40%+ revenue growth over the coming year. This highlights how digital self-service is no longer optional, but a baseline expectation for modern B2B buyers.
Pros | Cons |
|
|
Best for: Standardized B2B products with frequent repeat purchases.
If you’re planning to build a eCommerce site, it’s worth reviewing the best B2B eCommerce platforms to find the one that fits your business needs. Once you’ve chosen a platform, our migration service can help you move your data and operations smoothly.
Store Migration Made Easy With LitExtension!
LitExtension offers great migration solutions that help you transfer your data from the current eCommerce platform to a new one accurately, painlessly with utmost security.

Indirect/Partner Sales Channels
While direct sales focus on owning the customer relationship end to end, many B2B companies rely on partners to extend reach and scale faster. Indirect sales channels come into play when market coverage, local presence, or specialized expertise matters more than direct control.
Below are the indirect B2B sales channels most commonly used to support growth in practice.
4. Distributors
In a B2B context, distributors are third-party companies you work with to bring your products to market. They purchase from you, hold inventory, and resell to other businesses, often handling logistics, local sales, and fulfillment in the process.
You typically turn to distributors when reaching the market yourself becomes inefficient. If your customers are spread across regions or if logistics and local presence are difficult to manage internally, distributors help you scale faster by leveraging existing networks. In many cases, they also take on operational responsibilities that would otherwise slow your growth.
Pros | Cons |
|
|
Best for: Physical, high-volume B2B products that need broad geographic reach and efficient distribution.
5. Value-added resellers (VARs)
Some B2B products only deliver real value after they are adapted to a specific business context. That is where value-added resellers come in. Instead of focusing purely on distribution, VARs extend your product by layering services such as customization, implementation, training, or ongoing support.
In this model, sales success is often measured less by speed and more by adoption. Buyers work with partners who understand their industry requirements and can translate your product into a usable solution. For your business, this reduces the burden of building deep vertical or technical expertise internally while improving time-to-value for customers.
Pros | Cons |
|
|
Best for: B2B products that require configuration, integration, or hands-on services to deliver full value.
6. System integrators (SIs)
System integrators are partners you work with when customers don’t just buy a product, but expect someone to make everything work together. Their role goes beyond selling or reselling, as SIs take responsibility for setting up, integrating, and deploying your solution within a broader project scope.
You can think of large enterprises that already use many tools and systems. Rather than working directly with you to piece everything together, they often rely on a trusted integrator to manage the entire project. The SI brings your product into the picture, fits it into the customer’s existing setup, and stays involved until the solution is fully up and running.
Pros | Cons |
|
|
Best for: B2B products sold as part of large, multi-step projects rather than simple standalone purchases.
7. Referral & affiliate partners
Referral and affiliate partners are individuals or businesses that introduce you to potential customers rather than selling on your behalf. Instead of handling the sales process, they act as a source of warm introductions, typically motivated by commissions or incentives tied to successful deals.
According to the B2B Sales Benchmark Report 2024 by Ebsta, partnership-led deals move 3.8× faster from pipeline to revenue compared to outbound, inbound, and paid B2B sales channels. This means partnerships tend to generate fewer but higher-quality opportunities that convert more quickly and with less friction.
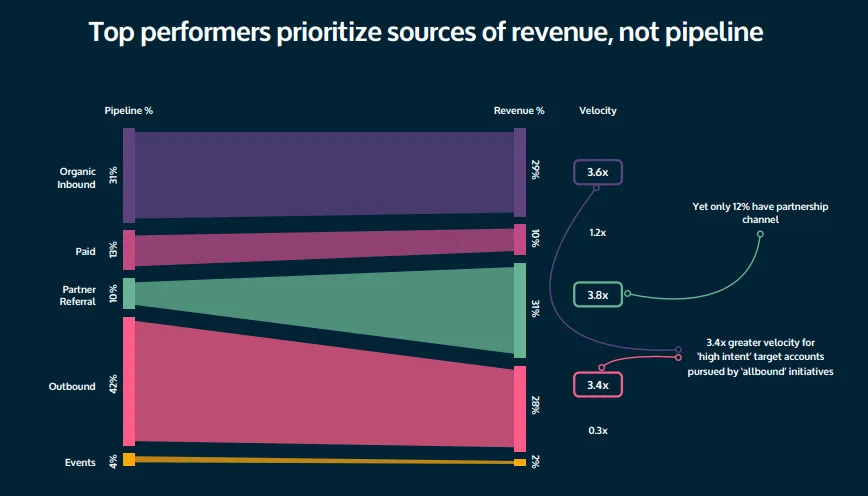
Based on these pros and cons, you can assess whether this channel aligns with your business goals and sales motion.
Pros | Cons |
|
|
Best for: Nearly all B2B businesses, when used as a supporting channel rather than a primary growth engine.
8. OEM partnerships
Another B2B sales channel you can consider is an OEM partnership, where your product is embedded into another company’s solution and sold alongside it. This approach allows your product to be delivered through the OEM’s distribution channels without requiring individual sales or implementation for each deal.
A simple way to think about this model is product inside product. For example, Intel does not sell processors directly to end users. Its chips are embedded in laptops sold by manufacturers like Dell. Customers buy Dell’s product, while Intel scales through volume as more devices are sold.

This is what clearly separates OEM partnerships from system integrators. While SIs sell projects and manage implementations, OEM partners sell finished products with your solution already built in.
Pros | Cons |
|
|
Best for: B2B products or components that deliver the most value when embedded into another product rather than sold independently.
Digital & Marketing Channels for B2B Sales
Once direct and partner channels are in place, the next question becomes how buyers find you in the first place. Across B2B sales channels, digital and marketing efforts influence demand well before teams start engaging buyers directly.
9. Content marketing & SEO
According to research from the Content Marketing Institute, nearly all B2B marketers actively use content as part of their marketing strategy, showing that content is no longer experimental but a standard practice across the market. The real challenge today is not whether to do content, but how to make it actually support revenue.
In practice, B2B content works best when it speaks directly to how buyers actually make decisions. Teams tend to see stronger results from fewer, more focused pieces that help prospects compare options, understand use cases, and build internal buy-in.
SEO then helps this content reach the right audience at the right moment. Most B2B buyers rely on search engines when researching products or services, and organic search consistently proves its value at the bottom of the funnel. In aggregated 2025 benchmarks, organic search averages around a 5.0% conversion rate, often outperforming several paid channels on a last-click basis.
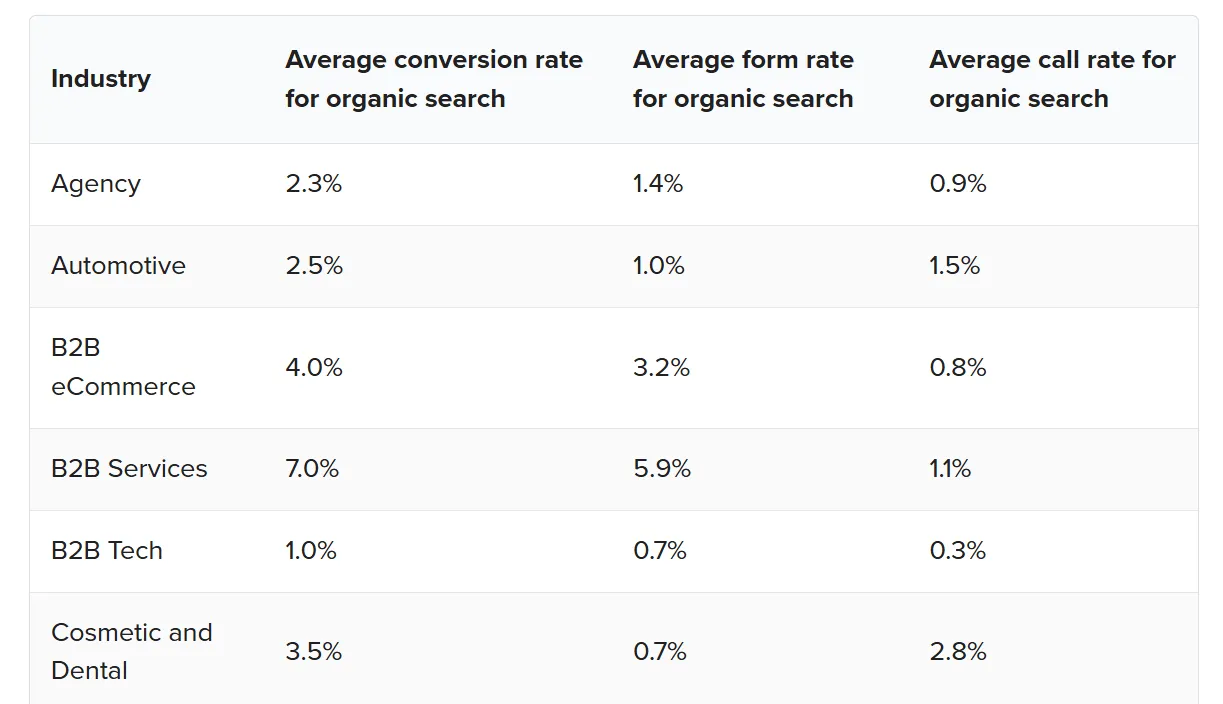
This is why SEO is not optional. It ensures your content shows up when buyers are actively evaluating solutions, turning visibility into real pipeline impact. “Despite the claims that SEO is dead, it's very much alive. Companies ranking in search results generate revenue, which is why it's such an important channel,” says David from a Brisbane focused search ranking agency.
Pros | Cons |
|
|
Best for: B2B businesses with research-heavy buying journeys that want to build sustainable, inbound demand over time.
10. Email marketing
Compared to search-driven B2B sales channels, email marketing leans more toward nurturing. It focuses on developing existing interest over time – educating leads, aligning buying committees, and supporting sales conversations throughout longer decision cycles.
HubSpot uses email marketing to support B2B sales by segmenting leads by lifecycle stage, behavior, and intent. Prospects receive targeted emails tied to specific actions, such as downloading a guide or attending a webinar. This approach keeps prospects informed and engaged over time, allowing sales teams to step in when intent is stronger and conversations are more productive.
Pros | Cons |
|
|
Best for: B2B businesses with repeat usage, subscription-based offerings, or clear expansion paths.
11. Social media marketing
In B2B, social media is rarely a direct sales channel. Its main role is to support awareness, credibility, and trust throughout a long buying journey, often long before buyers are ready to speak with sales. Most interactions on social platforms happen quietly, with buyers observing content rather than actively engaging.
According to Forrester’s report, LinkedIn clearly led other social platforms for B2B initiatives in 2024. This makes sense given LinkedIn’s professional environment, where decision-makers and buying group members actively consume business-focused content as part of their work.
That said, other platforms still matter in different ways. YouTube supports longer-form educational content, product explanations, and thought leadership. Facebook and X help maintain brand visibility and retargeting touchpoints, especially when paired with paid distribution. Together, these platforms reinforce presence and familiarity while buyers research options and build internal alignment.
Pros | Cons |
|
|
Best for: B2B businesses that want to reinforce brand credibility, support other sales channels, and stay visible throughout long buying journeys.
12. Online marketplaces
To continue our list of the best B2B marketing channels, we must include online marketplaces. Selling through online marketplaces means listing your products or services on third-party platforms where buyers already come with clear purchasing intent. Instead of driving demand yourself, you tap into existing traffic and infrastructure, with the marketplace handling discovery, payments, and often fulfillment.
In many cases, Amazon Business and Alibaba tend to work well for standardized products with clear pricing and specifications. Meanwhile, industry-specific marketplaces often perform better for niche or regulated categories.

Because of that, we usually recommend focusing on the marketplace that best matches your buyers, rather than trying to show up everywhere.
Pros | Cons |
|
|
Best for: B2B businesses selling standardized or clearly defined products to buyers who are ready to purchase and value speed and convenience.
13. Paid advertising
When you decide to use paid advertising, the process usually starts with a very specific goal. This might be driving traffic to a landing page, promoting a piece of high-intent content, supporting a product launch, or testing demand from a defined group of companies.
Most B2B teams still rely on familiar platforms such as Google Ads, LinkedIn Ads, and Facebook Ads. What has changed is how these platforms operate behind the scenes. According to Google Ads documentation, AI-driven bidding now optimizes campaigns in real time based on user intent and behavioral signals, rather than static keyword rules.
Because of this shift, paid advertising requires closer, more frequent adjustments. Brands need to evolve faster, budgets need to move based on real performance signals, and campaigns work best as short-cycle experiments rather than set-and-forget channels. When used this way, paid ads support sales teams instead of trying to replace them.
Pros | Cons |
|
|
Best for: B2B businesses that need fast visibility, short-term demand, or tactical support for specific campaigns.
14. Livestream product demos
This is one of those B2B sales channels that focuses on showing, not explaining. Teams typically walk through real workflows, handle questions as they come up, and demonstrate how the product performs in realistic scenarios. Because everything happens live, prospects get a clearer sense of usability, limitations, and fit without the polish of pre-recorded content or slide-heavy presentations.
Livestream demos are especially effective as a sales-support tool. They help remove uncertainty late in the decision process, align multiple stakeholders around the same view of the product, and speed up internal buy-in. Rather than driving volume, their real value lies in helping qualified prospects move forward with confidence.
Pros | Cons |
|
|
Best for: B2B products where buyers need to see real workflows and functionality before committing, especially during late-stage evaluation.
Events & Relationship-Based B2B Sales Channels
When B2B deals get bigger and more complex, sales often move beyond pure digital tactics. At this stage, trust, credibility, and human connection start to matter just as much as reach. That’s where relationship-driven B2B sales channels come into play.
15. Trade shows & industry events
Trade shows and industry events are where B2B relationships often begin offline. These environments give prospects a chance to see your product, ask detailed questions, and evaluate your team face-to-face. For complex solutions, that in-person context can accelerate trust far faster than emails or ads ever could.

More importantly, events concentrate the right audience in one place. You’re not just selling – you’re listening, learning market signals, and positioning your brand among peers. And once those first conversations happen in person, following up digitally becomes much easier and warmer.
Pros | Cons |
|
|
Best for: B2B products in enterprise software, manufacturing, logistics, or industrial solutions where buyers expect in-person demos and direct discussions.
16. Webinars & on-demand events
While physical events create depth, webinars help you scale that same expertise online. They allow you to educate, demonstrate, and engage with prospects without geographic limits. For many B2B teams, webinars act as a bridge between awareness and serious sales conversations.

On-demand formats extend that value even further. A strong webinar can keep generating qualified leads long after the live session ends. When prospects choose to spend 30–60 minutes learning from you, they’re already signaling intent – which makes subsequent sales outreach far more relevant and welcomed.
Pros | Cons |
|
|
Best for: SaaS platforms, cloud services, fintech, and consulting solutions that need explanation, education, and use-case storytelling.
17. Customer referrals & word-of-mouth
While word-of-mouth is often associated with B2C, in B2B it functions as a trust-based sales channel rooted in professional relationships.
Once trust is established, one of the most powerful B2B sales channels often isn’t something you actively “run” at all. Customer referrals and word-of-mouth come naturally when your product delivers real value. In B2B, a recommendation from a peer carries far more weight than any marketing message.

Referrals also tend to shorten sales cycles. Prospects come in with higher confidence, clearer expectations, and fewer objections. While you can’t force referrals, you can design experiences – through onboarding, support, and success milestones – that make customers genuinely want to recommend you.
Pros | Cons |
|
|
Best for: Agencies, IT services, consulting firms, and niche B2B providers where trust and reputation drive buying decisions.
18. Professional networks
Finally, long-term B2B sales are built on professional networks. These include industry communities, alumni groups, founder circles, and peer-to-peer networks where relationships grow over time rather than through direct selling.
What makes this channel valuable is consistency. By showing up, contributing insights, and being helpful without pitching, you stay top-of-mind. Over time, opportunities emerge organically – often as introductions, partnerships, or inbound inquiries that feel far more natural than cold outreach.
Pros | Cons |
|
|
Best for: Founder-led companies, professional services, and partnership-driven B2B businesses focused on long-term growth.
Summary: B2B Sales Channels Covered in This Guide
B2B sales channels are the different ways businesses reach, engage, and sell to other businesses. In this guide, we’ve grouped the most common channels based on how sales conversations are initiated and how buyers prefer to evaluate solutions.
Direct Sales Channels
- In-house sales team: Internal sales reps handle direct conversations, demos, negotiations, and deal closing with business buyers.
- Outbound sales: Proactive outreach through cold emails, calls, or LinkedIn to initiate conversations with target accounts.
- B2B eCommerce site: A company-owned online storefront that enables self-service ordering, pricing visibility, and account management.
Indirect & Partner Sales Channels
- Distributors: Third-party companies that purchase products in bulk and resell them through their own networks.
- Value-added resellers (VARs): Partners that bundle your product with additional services, customization, or industry expertise.
- System integrators (SIs): Partners responsible for implementing, integrating, and rolling out solutions as part of larger projects.
- Referral & affiliate partners: Partners or customers who introduce your solution to new buyers in exchange for incentives or commissions.
- OEM partnerships: Arrangements where your product is embedded into another company’s offering and distributed at scale.
Digital & Marketing Channels for B2B Sales
- Content marketing & SEO: Educational content that attracts inbound leads and supports buyers during research and evaluation.
- Email marketing: Lifecycle-based communication used to nurture leads and support sales readiness.
- Social media marketing: Platforms like LinkedIn, YouTube, Facebook, and X that influence awareness and credibility.
- Online marketplaces: Third-party platforms such as Alibaba or Amazon Business that connect sellers with large buyer audiences.
- Paid advertising: Performance-driven campaigns on platforms like Google Ads and LinkedIn Ads to support demand generation.
- Livestream product demos: Live or recorded sessions that showcase products, workflows, or use cases in real time.
Events & Relationship-Based Sales Channels
- Trade shows & industry events: In-person events that support trust-building, networking, and late-stage deal acceleration.
- Webinars & on-demand events: Scalable formats for education, product explanation, and lead qualification.
- Customer referrals & word-of-mouth: Buyer-to-buyer recommendations that bring in high-trust, high-intent leads.
- Professional networks: Industry communities and peer groups where long-term relationships lead to organic opportunities.
How to Choose the Right B2B Sales Channels for Your Business?
Up to this point, we’ve walked through a wide range of channels to increase B2B sales – from direct and indirect to marketing and relationship-driven approaches. With so many options on the table, it’s easy to feel unsure about which channels actually fit your business. The infographic highlights four core considerations that help guide B2B sales channel selection.

Below, we break each consideration down in plain terms so you can apply them more easily to your own business:
- Understand your buyers: Know who your buyers are, how they research, and when they expect to talk to sales.
- Align channels with deal size and complexity: Complex, high-value deals need relationship-driven channels, while simpler deals scale better through inbound or self-service.
- Factor in your internal resources: Choose channels your team can run consistently based on budget, capacity, and skills.
- Use a combined channel approach: Strong B2B strategies blend multiple channels across different stages of the buyer journey.
These four points are meant to guide your thinking, not limit it. Start with what fits your business today, then adjust your channel mix as your sales motion evolves.
B2B Sales Channels: FAQs
What are the best b2b sales channels?
The best B2B sales channels depend on deal size, sales complexity, and target buyers. For high-value or complex solutions, direct sales, events, webinars, and referrals tend to perform best. For simpler or scalable offerings, inbound channels like content marketing, SEO, and email nurturing often deliver stronger results.
What are the channels of B2B marketing?
Common B2B marketing channels include content marketing, SEO, paid advertising, email marketing, social media, webinars, events, partnerships, and account-based marketing (ABM). These channels focus on generating awareness, educating buyers, and supporting sales teams rather than driving instant purchases.
Which B2B sales channels work best for small businesses?
Small businesses should prioritize high-leverage, low-cost channels. These include inbound, referrals, professional networks, and targeted outbound outreach. They require lower upfront investment, rely more on expertise and relationships, and allow teams to compete without large marketing budgets.
Can B2B sales channels be combined?
Yes, combining B2B sales channels is not only possible but often necessary. Many successful teams use inbound marketing to attract leads, webinars to educate them, outbound sales to follow up, and referrals to accelerate trust. A multi-channel approach helps cover different stages of the buyer journey.
How do companies decide between direct and indirect B2B sales channels?
Companies usually choose direct sales when deals are complex, high-value, or require close customer relationships. Indirect channels, such as partners or resellers, are often used when scale, geographic reach, or faster market entry is the priority. The decision depends on control, cost, and customer expectations.
How does deal size and sales complexity influence which B2B sales channels perform best?
Larger deal sizes and higher sales complexity typically favor relationship-driven channels like direct sales, events, and referrals. Smaller deals or standardized products perform better with scalable channels such as inbound marketing, self-serve demos, or inside sales. As complexity increases, buyers usually expect more human interaction and guidance.
Conclusion
There is no single “best” B2B sales channel that works for every business. What matters most is how well each channel aligns with your buyers, deal size, and sales complexity. The strongest B2B teams don’t rely on one tactic alone, but build a balanced mix of channels that support the entire buyer journey.
We hope this article has helped clarify how different B2B sales channels work and how to choose the ones that fit your business best. With the right channel mix in place, selling becomes less about trial and error and more about consistent, intentional growth.
For more growth tips, head to our blog posts or join our community group to share with other eCommerce fellows.

