Data loss can happen when you least expect it, whether from human error, system failures, or unexpected outages. That’s why having a reliable SQL backup strategy is essential if you want to protect your data and recover quickly when problems occur.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll walk you through để methods & best practice thôi nhén:
- How to backup with SQL Server Management Studio;
- How to backup SQL database using Transact-SQL (T-SQL);
- Steps to backup Azure SQL database;
- Best practices to run backup SQL database like a pro.
Let’s get started!
SQL Backup Explained: Quick Overview
SQL backup is the process of creating a copy of your database so it can be restored if data is lost, damaged, or accidentally changed. This backup is stored separately from the original database, so you can recover information when something goes wrong.
As a database grows and changes over time, backups become essential for recovery and long-term data protection. You may add new records, update existing data, or run automated processes in the background. Even a small mistake or system error can lead to unexpected problems. With a proper SQL backup in place, you can restore data faster, reduce downtime, and avoid disruptions to your work or business operations.
In practice, SQL backups are typically used in the following situations:
- System failures: server crashes or software errors that impact database stability.
- Disaster recovery: outages, security incidents, or infrastructure issues that disrupt normal access to data.
- Rollback scenarios: restoring the database to an earlier state after accidental deletions or incorrect updates.
SQL Backup Types: What You Actually Need to Know
When people talk about SQL backups, they’re usually referring to a few core backup types that work together to protect your data. You don’t need to understand every technical detail, but knowing how each type functions will help you choose a backup approach that fits your system and how often your data changes.
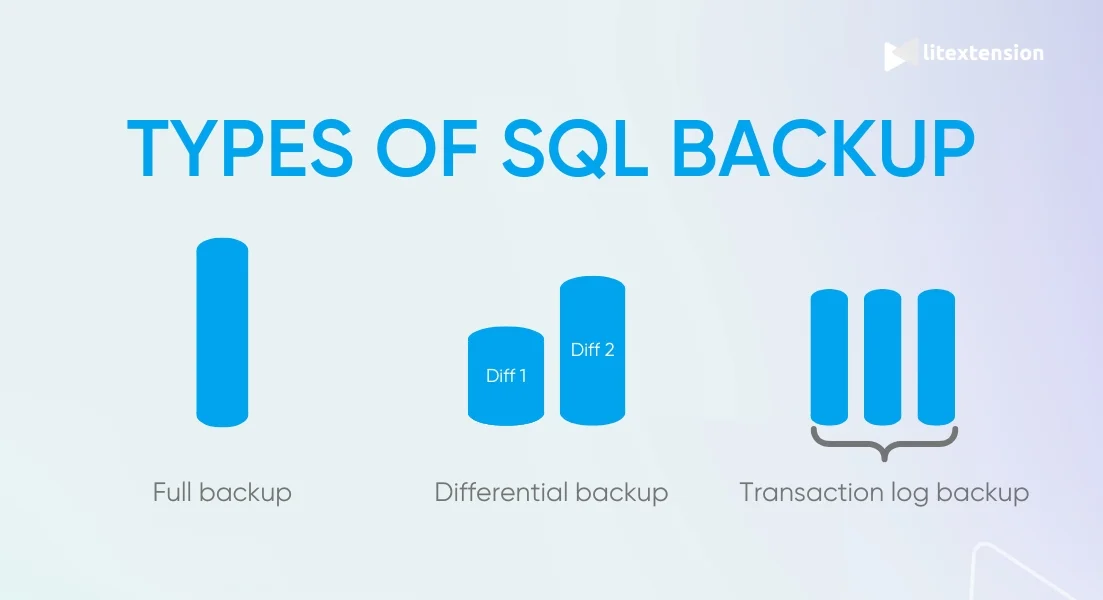
Full backup
A full backup is the most complete form of database protection. It captures the entire database at a specific point in time, including all data, tables, and structure. The main trade-off is that it requires more time and storage to run. For this reason, full backups are usually scheduled less frequently, often during off-peak hours.
Differential backup
Instead of copying the entire database again, a differential backup includes only the data that has changed since the last full backup. Because it saves newly added or updated information, this type of backup runs faster and uses less storage. During recovery, you typically restore the latest full backup and then apply the most recent differential backup, keeping the process simple and efficient.
Transaction log backup
Last but not least, transaction log backups record individual database transactions as they occur, allowing you to restore data to a specific point in time if needed. These backups are usually small and run often, but they depend on an existing full backup and follow a more structured restore sequence.
How these backups work together:
In a SQL backup strategy, these backup types are rarely used on their own. You might rely on a full data backup as your base, use differential backups to capture daily changes, and run transaction log backups throughout the day to track ongoing activity. Together, they help balance storage usage, backup speed, and recovery flexibility.
How to Backup SQL Using SQL Server Management Studio
SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) provides a user-friendly, graphical interface for performing SQL backups. This solution makes it easy for users to configure and schedule backups without the need for complex commands. Therefore, this method is ideal for those who prefer a visual approach over command-line operations.
Before beginning, ensure that:
- SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) is installed.
- You have administrative access to the SQL server.
- You have permission to create backups on the database.
Here's how to back up an SQL database using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
Step 1: Launch SSMS and log in to the server where your database is stored.
Step 2: Expand the ‘Databases' folder in the ‘Object Explorer' to see a list of available databases.
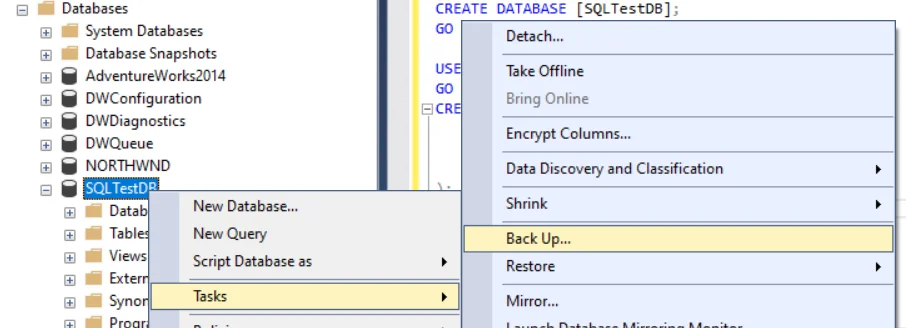
Step 3: Right-click the database you want to back up, hover over ‘Tasks', and select ‘Back Up'.
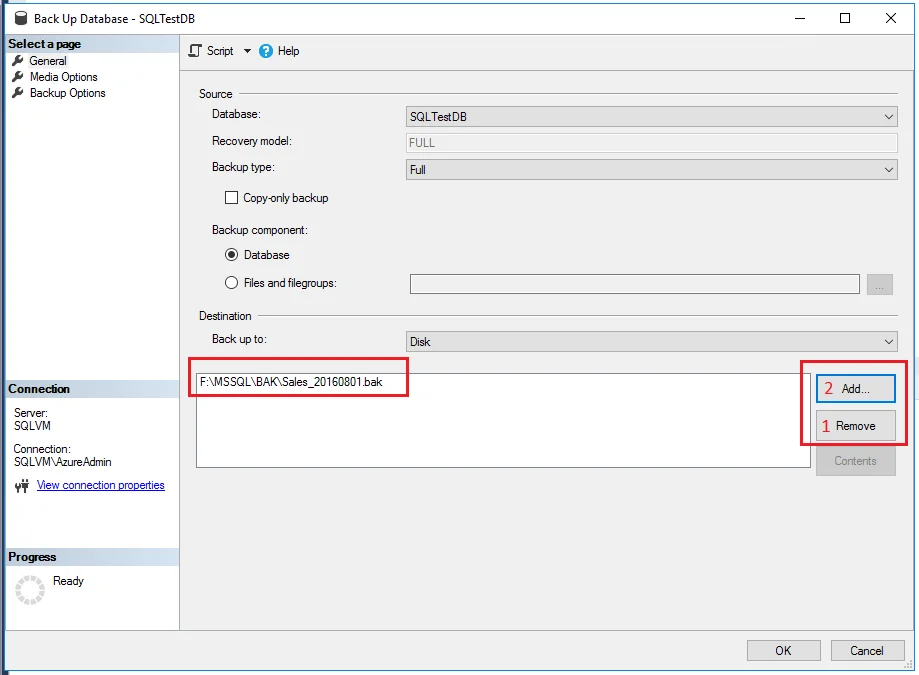
Step 4: From the ‘Back Up Database' window, select the ‘Backup type' from the drop-down list.
Step 5: Then, in the ‘Destination' section, click ‘Add', then select the folder and enter the file name, ensuring it ends with a ‘.bak' extension. In case you accidentally added the wrong path, you can delete it using the ‘Remove' button.
Step 6: Click ‘OK' to start the backup process. A message will appear confirming the backup’s success when it’s complete.
How to Backup a SQL Database Using Transact-SQL (T-SQL)
While SSMS is ideal for users who prefer a visual interface, some scenarios require a script-based approach. In this section, we’ll look at how to back up a SQL database using Transact-SQL commands.
Before running any T-SQL backup commands, make sure the following requirements are met:
- You’re using SQL Server (these commands do not apply to MySQL or PostgreSQL)
- The SQL Server service account has write permission to the backup folder (for example, D:\SQLBackups)
- You’re running the commands in a tool that supports T-SQL, such as SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), Azure Data Studio, or sqlcmd
Open a New Query window and use the following command. This version includes Compression, which is highly recommended for saving disk space and improving performance.
BACKUP DATABASE [YourDatabaseName] TO DISK = N'D:\SQLBackups\YourDatabaseName_full.bak' WITH NOFORMAT, NOINIT, NAME = N'YourDatabaseName - Full Database Backup', STATS = 10; GO
At this point, you’ll need to replace the following values to match your environment:
- [YourDatabaseName]: Replace this with the exact name of the database you want to back up.
- D:\SQLBackups\…: Update the path to a valid directory on your server's local storage or a mapped network share.
- NAME: Adjust this string to make the backup easily identifiable when viewing backup history.
After the command completes, check the Messages tab in your query editor. It should display:
BACKUP DATABASE successfully processed X pages in Y seconds.
You can then navigate to your backup folder to confirm the .bak file is present.
How to Backup an Azure SQL Database?
Azure SQL Database follows a cloud-native model that differs from traditional on-prem SQL Server backup database methods. Instead of managing backup files yourself, Azure handles most backup operations automatically, while still offering a manual export option when you need a downloadable copy.
Automated backups
By default, Azure SQL Database runs automated backups continuously in the background. These SQL backups require no manual configuration and are used by Azure to support restore scenarios such as point-in-time recovery or restoring the database as a new instance.
Specifically, Azure SQL Database creates:
- Full backups every week.
- Differential backups every 12 or 24 hours.
- Transaction log backups approximately every 10 minutes.
The exact frequency of transaction log backups depends on your database’s compute size and activity level. When you restore a database, Azure automatically determines which full, differential, and transaction log backups are required to recover the database to the selected point in time.
With this approach, you don’t need to manage backup schedules, storage paths, or backup files. However, these automated backups cannot be accessed or downloaded directly and are only available for restore operations within Azure.
Exporting an Azure SQL Database
If you need a portable backup for archiving, offline storage, or migration, you can export your database into a BACPAC file. Unlike a standard .bak file, a BACPAC contains both the database schema and the data.
Before starting the export, ensure your environment meets these specific Azure requirements:
- Transactional consistency: Azure SQL doesn't “freeze” the database during export. To ensure a consistent backup, stop all write activity or export from a database copy or point-in-time restore.
- Size limits: Exports directly to Azure Blob Storage via the portal are limited to 200 GB. For larger databases, use the SqlPackage command-line utility.
- Naming rules: The BACPAC filename must be fewer than 128 characters, cannot end with a period, and must avoid special characters (e.g., < > * % & : \ / ?) or spaces.
- Timeouts: If the export takes longer than 20 hours, Azure may cancel the operation.
- Performance: For large databases, temporarily scale up your Service Tier (DTUs/vCores) to speed up the data extraction process.
With these requirements met, you’re ready to start the export process. The following steps show how to export an Azure SQL Database through the Azure portal.
Step 1: Sign in to the Azure portal and navigate to the page for your Azure SQL Database. On the database toolbar, click Export.
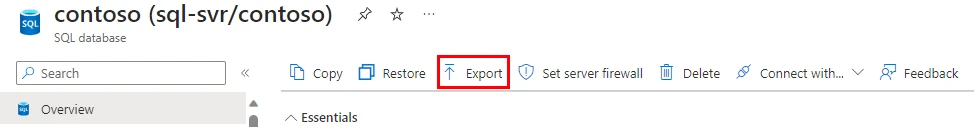
Step 2: In the Export database pane, specify a file name for the BACPAC. You can select an existing Azure storage account and container where the BACPAC will be stored.
Step 3: Enter the SQL admin credentials (a SQL Server admin login is required to export).
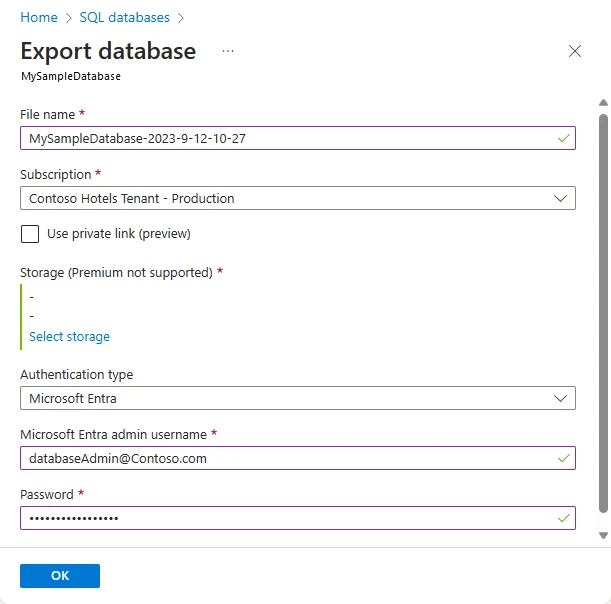
Step 4: Click OK to start the export.
Step 5: To monitor progress, go to the Import/Export history under the server’s Data management section.
After export completes, you can go to the storage account and container you chose and download the BACPAC file for offline use or migration.
When to Use Third-Party SQL Backup Tools? 4 Commonly Used Solutions
Third-party SQL backup tools are useful when built-in backup options are not enough for your system’s needs. They help simplify backup management while improving data security and recovery reliability.
These tools often include features such as automated scheduling, encryption, cloud storage, and performance optimization. As a result, they make it easier to manage backups for databases of all sizes, from small projects to enterprise environments.
Below are some commonly used SQL backup tools and services. Each option offers different features and pricing models, allowing you to choose a solution that fits your technical requirements and budget.
Cohesity
Cohesity is an advanced data management solution designed for enterprise environments requiring comprehensive backup, storage, and data protection features. Its platform provides a unified approach to backup by centralizing data management and making backups, recovery, and long-term storage more efficient.
Cohesity’s support for multiple environments, including on-premises, cloud, and hybrid setups, makes it highly versatile, especially for organizations with complex data needs. Additionally, Cohesity integrates security measures, like encryption and ransomware protection, to enhance data security and integrity.
Highlight features:
- Unified backup and recovery across cloud, on-premises, and hybrid environments
- Automated backup scheduling and policy-driven data management
- Advanced security features, including ransomware detection and data encryption
- Scalable architecture to support large datasets
- Fast recovery options with granular restore capabilities
Acronis
Acronis is a versatile backup and cybersecurity solution that serves a wide range of businesses, from small startups to large enterprises. Known for its strong security features, Acronis combines backup with cybersecurity, providing protection against ransomware and other threats. The platform supports SQL databases and offers a flexible backup frequency, with options for local, cloud, or hybrid storage.
Acronis is a popular choice for organizations needing a reliable, secure backup solution that’s easy to manage without sacrificing data protection.
Highlight features:
- Data encryption and ransomware protection for secure backups
- Flexible backup scheduling with options for continuous data protection
- Choice of local, cloud, or hybrid storage options
- Comprehensive backup and recovery for SQL databases
- Easy-to-use interface for managing backups and restoring data
Commvault
Commvault is an enterprise-grade backup and data management solution ideal for organizations handling large datasets and complex infrastructure. The platform provides powerful data protection capabilities, including AI-driven automation for more efficient backup processes.
Commvault supports multiple environments, making it suitable for both cloud and on-premises setups. Its advanced reporting and analytics give administrators in-depth insights into backup performance and storage efficiency, making it ideal for large businesses with complex data protection needs.
Highlight features:
- AI-driven data protection and automation for enhanced efficiency
- Support for multi-cloud and hybrid environments
- Comprehensive reporting and analytics for backup performance
- Granular recovery options to restore specific data points
- Scalable for handling high volumes of data
Red Gate
Red Gate is a specialized SQL Server backup tool designed with simplicity and efficiency in mind for SQL database administrators. Known for its ease of use, Red Gate provides automated SQL backups with features that simplify database management and help prevent data loss.
Red Gate integrates well with SQL Server environments and offers automated backup scheduling, encryption, and a user-friendly interface, making it an excellent choice for SQL Server administrators who want reliable and straightforward backup management.
Highlight features:
- Simple setup and configuration specifically for SQL Server
- Automated backup scheduling to streamline maintenance
- Encryption options for secure backup files
- Transaction log management to allow point-in-time recovery
- User-friendly interface for managing SQL backups and restorations
Best Practices for SQL Database Backups
A reliable SQL backup strategy is not just about creating backups. It’s about ensuring those backups are secure, recoverable, and aligned with how your data actually changes. The best practices below help minimize data loss, reduce downtime, and keep your backup process efficient over time.
1. Follow proven backup architecture principles
A backup architecture should match how frequently data changes and how quickly recovery is required. Most databases benefit from combining full, differential, and transaction log backups instead of relying on a single backup type.
This layered approach allows full backups to serve as a baseline while other backup types capture changes more frequently. As a result, recovery becomes more flexible without creating unnecessary storage overhead.
2. Automate and monitor backup operations
Automation helps ensure that backups run consistently and on schedule without manual intervention. Automated jobs reduce the risk of missed backups, especially in busy production environments.
Ongoing monitoring remains essential even with automation in place. Regularly reviewing backup logs helps identify failures, warnings, or performance issues before they impact recovery.
3. Secure and isolate backup storage
Backup files often contain sensitive information and require the same level of protection as production data. Encryption plays a key role in preventing unauthorized access, particularly when backups are stored outside the primary system.
Storage isolation also improves resilience. Keeping at least one backup copy separate from the production environment reduces the risk of losing both live data and backups during major incidents.
4. Test, verify, and document everything
Last but not least, backup reliability depends on successful restoration. Verifying backups after creation and performing test restores periodically confirm that recovery procedures work as expected.
Clear documentation supports faster response during incidents. Well-documented backup and restore processes help teams act confidently and consistently under pressure.
SQL Backup – FAQs
What is a backup in SQL?
A backup in SQL is a copy of your database that you create so you can recover your data if something goes wrong. This includes situations like accidental deletions, system failures, or data corruption. A backup allows you to restore the database to a previous, working state instead of losing data permanently.
What are the main 3 types of backups in SQL?
The three main types of SQL backup includes:
1. Full backup: Provides a complete snapshot of the entire database.
2. Differential backup: Saves only the changes made since the last full backup.
3. Transaction log backup: Capture all recent transactions, enabling point-in-time recovery and protecting data against frequent changes.
What is full backup in SQL?
A full backup in SQL is a complete copy of the entire database at a specific point in time. It includes all data, tables, and database structure. Full backups usually serve as the foundation for other backup types and are commonly created on a regular schedule, such as daily or weekly.
What is the difference between a differential and a transaction log backup?
A differential backup contains all changes since the last full backup. A transaction log backup captures all changes since the last log backup, allowing you to restore to a specific point in time.
How do I backup my SQL database?
You can back up a SQL database in several ways, depending on your setup:
- You can use SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) to create a backup through a graphical interface.
- You can run Transact-SQL (T-SQL) commands to create script-based backups.
- If you use Azure SQL Database, backups are created automatically, and you can export the database manually when needed.
The best method depends on whether you prefer a visual tool, command-based control, or a fully managed cloud solution.
Final Words
SQL backups are essential to any data management strategy, providing a safety net for businesses by safeguarding critical data and ensuring smooth recovery in the event of data loss or system failures. Implementing a solid SQL backup plan can significantly reduce downtime, protect data integrity, and allow for flexible recovery options tailored to your organization’s needs.
We hope that this article has guided you through the whole backup process clearly. If you like this blog, don't forget to check out other articles about shopping cart migration or join our community group to get more tips and guide.